
Part 5 - Settings
The 'Safety Settings' section is specifically crafted to acquaint users with critical safety-related configurations and options within the ECDIS (Electronic Chart Display and Information System). This module aims to empower users with the knowledge and skills required to optimize safety measures during maritime navigation.
By delving into the 'Safety Settings', users will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to configure alarms, alerts, and monitoring features that are vital for ensuring a secure and controlled maritime experience. The content in this section will walk you through the intricacies of setting up safety parameters, such as area alarms, route monitoring, and water level adjustments.
Upon completing this module, users will be equipped with the confidence and proficiency to navigate the safety settings of the ECDIS seamlessly. The provided information and guidance will contribute to enhancing users' ability to use the ECDIS system effectively, fostering a safer and more secure maritime navigation environment.
By delving into the 'Safety Settings', users will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to configure alarms, alerts, and monitoring features that are vital for ensuring a secure and controlled maritime experience. The content in this section will walk you through the intricacies of setting up safety parameters, such as area alarms, route monitoring, and water level adjustments.
Upon completing this module, users will be equipped with the confidence and proficiency to navigate the safety settings of the ECDIS seamlessly. The provided information and guidance will contribute to enhancing users' ability to use the ECDIS system effectively, fostering a safer and more secure maritime navigation environment.
5.4. Safety Settings
>
>
5.4. Safety Settings
The currently examined element is indicated by a green outline and numbering. Explanations will be provided in this window. After reviewing the information, click the 'Next' button or follow the instructions. If you wish to go back to the previous step, click 'Back'. If you decide to finish the study prematurely or choose another section, click 'End'.
Message
0
1
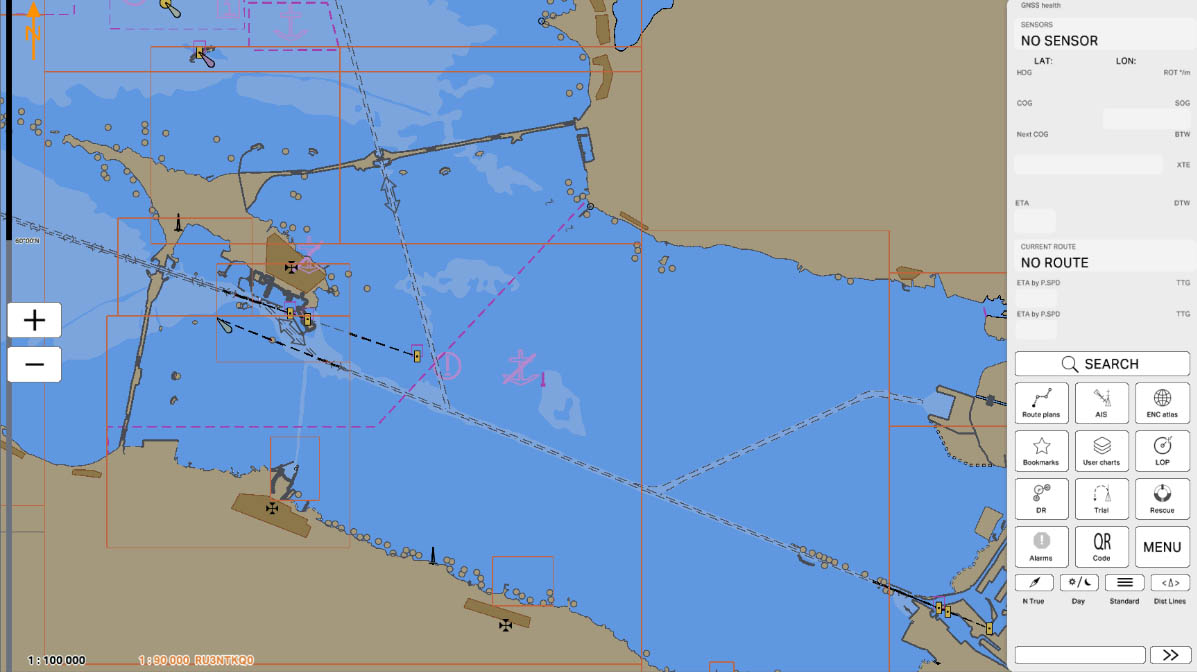
In the 'MENU' section, you'll find a list of program settings. This section allows users to customize and adjust various parameters according to their preferences and operational needs. Configuring these settings is essential for tailoring the program to specific requirements and ensuring optimal functionality.
Click on the 'MENU' icon to open Config menu.
Click on the 'MENU' icon to open Config menu.
MENU
3
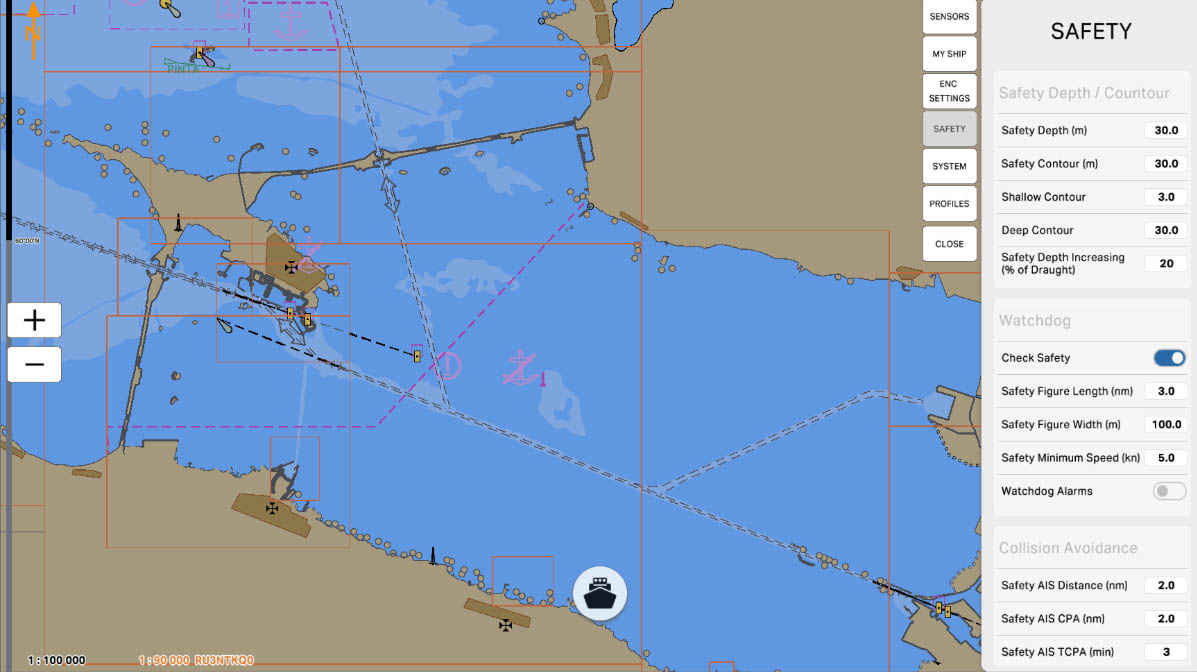
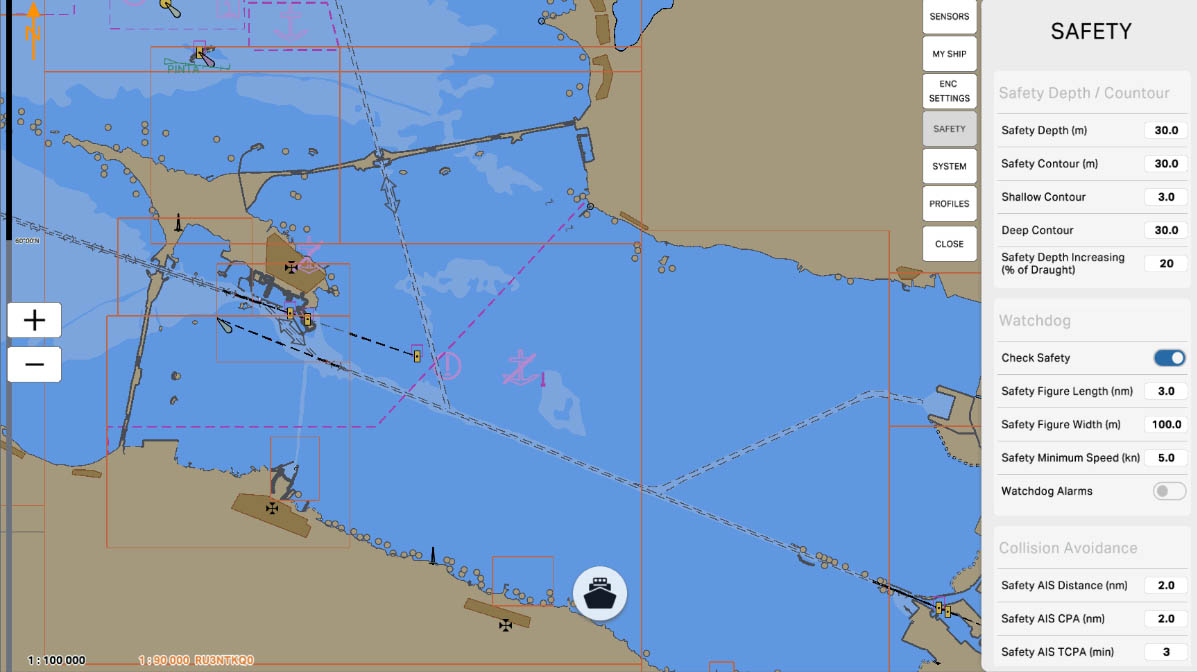
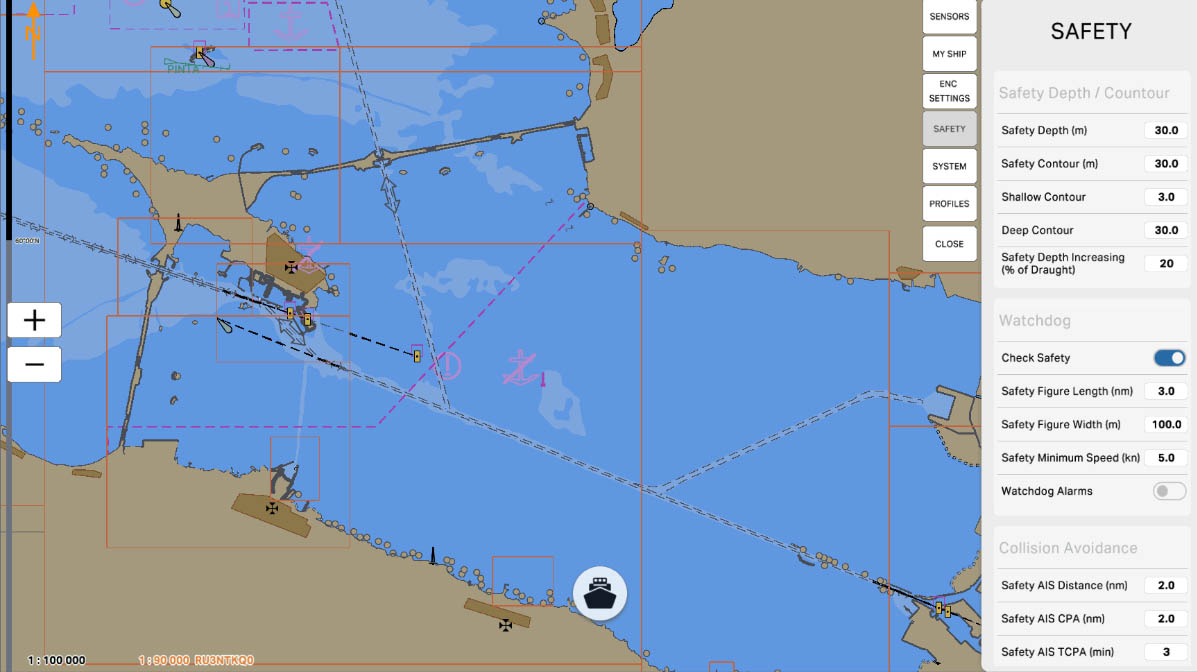
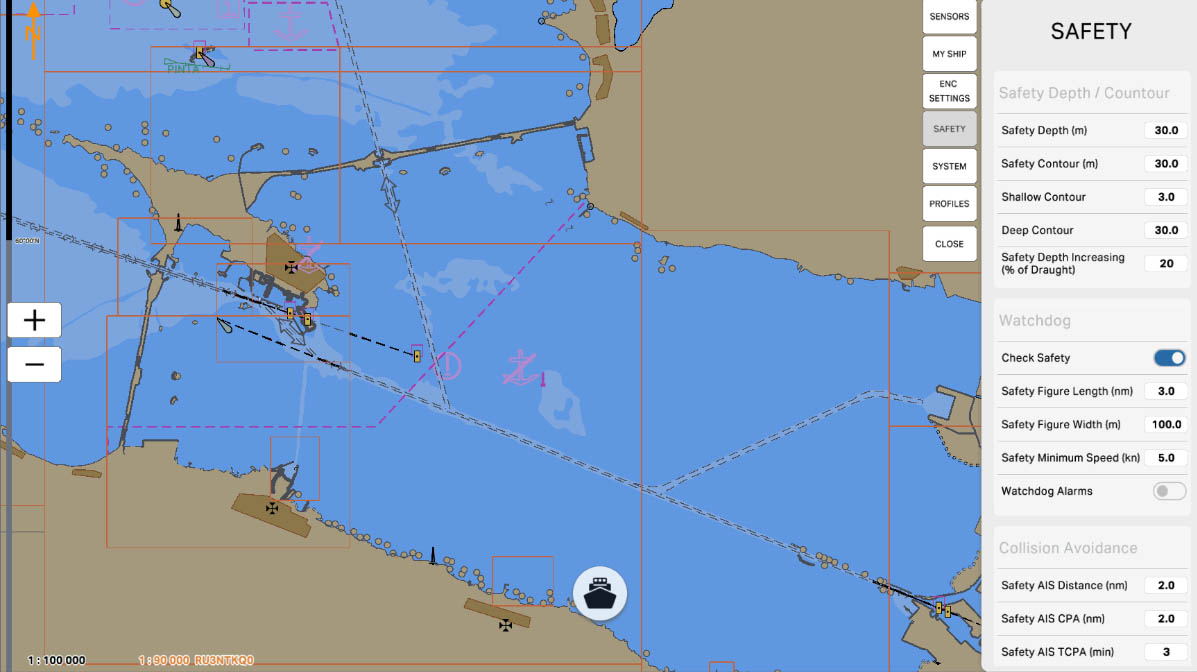
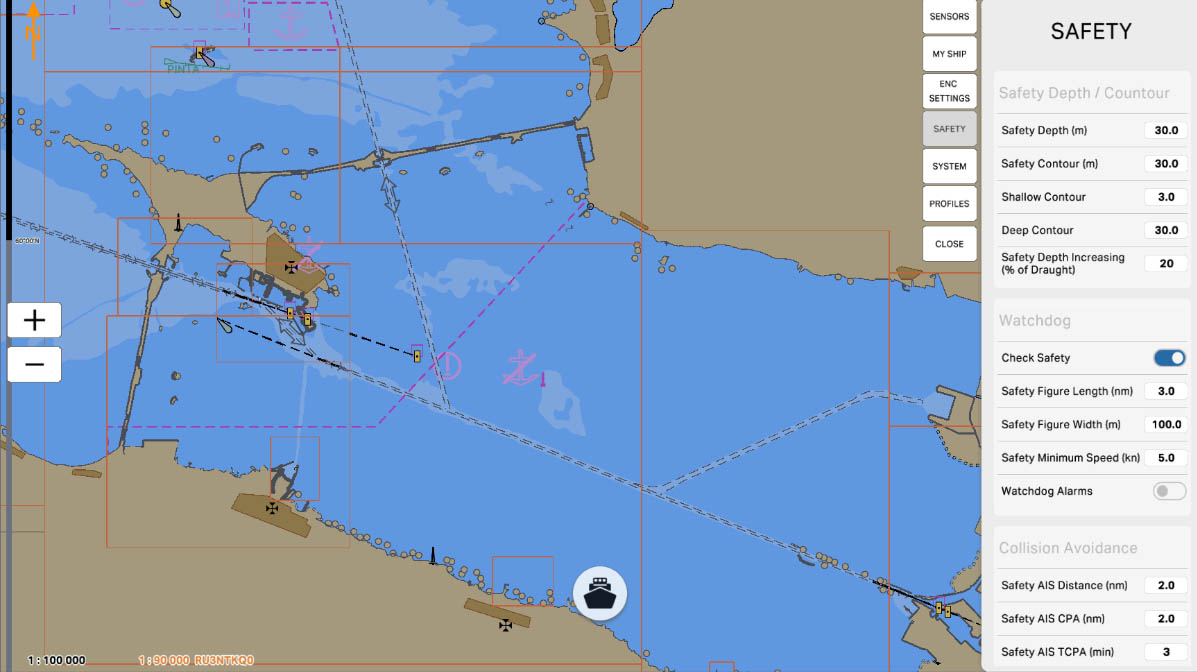
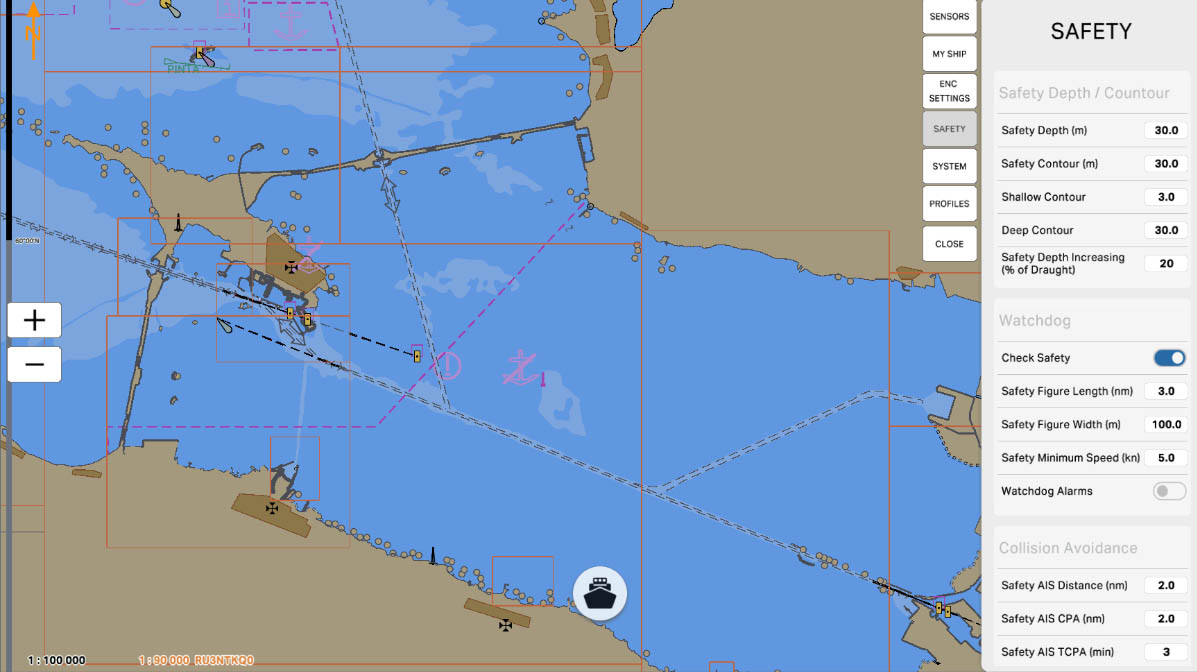
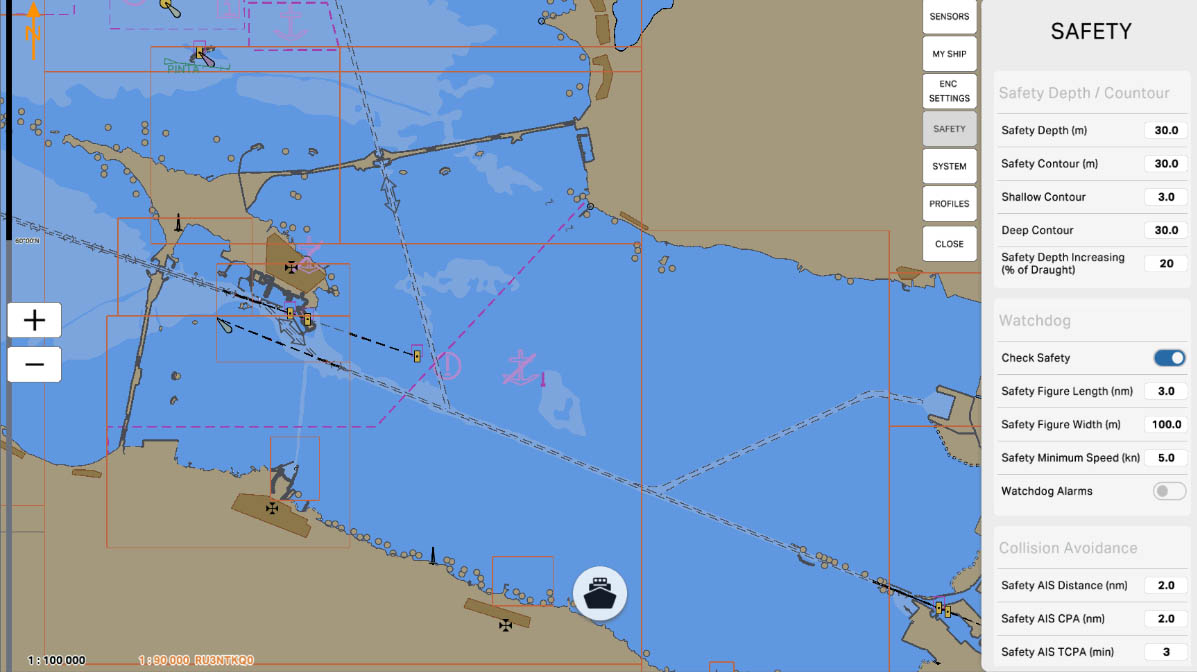
The 'Safety Depth/Contour' setting in the Safety Settings section of ECDIS (Electronic Chart Display and Information System) allows mariners to define which depths are considered safe and visually highlight these areas on the chart. This is crucial for preventing maritime accidents and ensuring safe navigation in specific maritime conditions.
SAFETY SETTINGS
4
The 'Safety Depth (m)' setting allows specifying a specific depth in meters that the vessel considers safe for navigation. This value is used to identify safe areas on the nautical chart, visually highlighted to facilitate navigation and prevent potential hazards.
Safety Depth/Contour
5
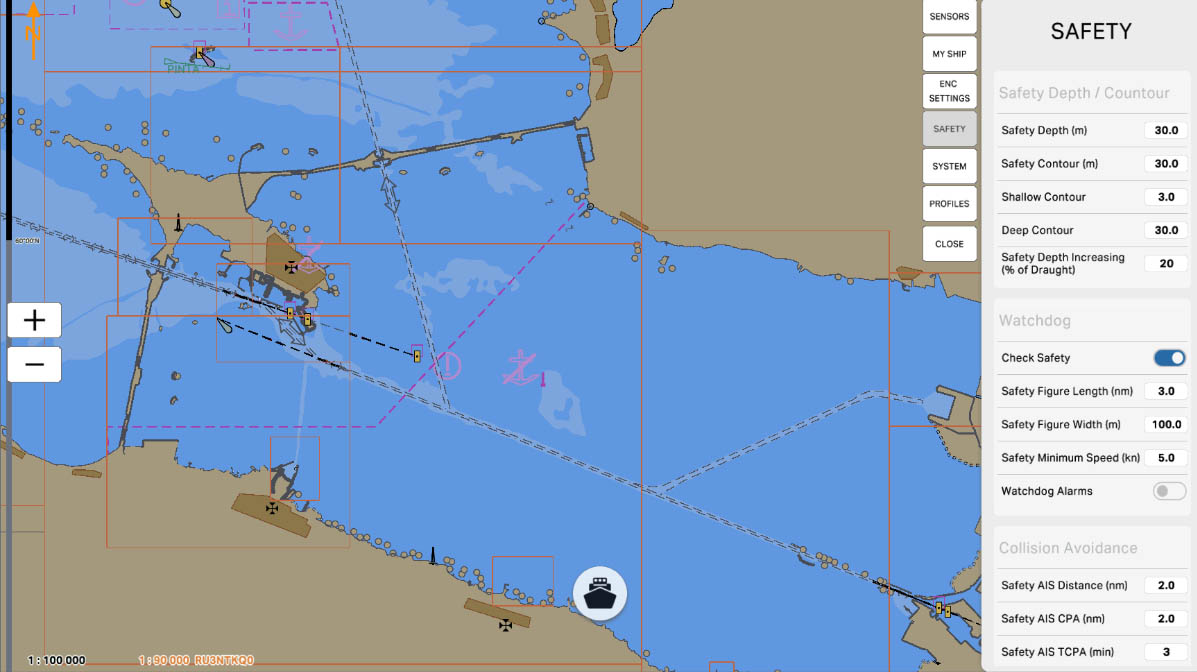
The 'Safety Contour (m)' setting allows you to specify a particular depth in meters that serves as the boundary for a safe area on the nautical chart. This contour visually highlights the area within which a vessel is considered safe for navigation. This is a crucial parameter to ensure the safety of vessels in various maritime conditions and prevent potential hazards.
Safety Depth/Contour
6
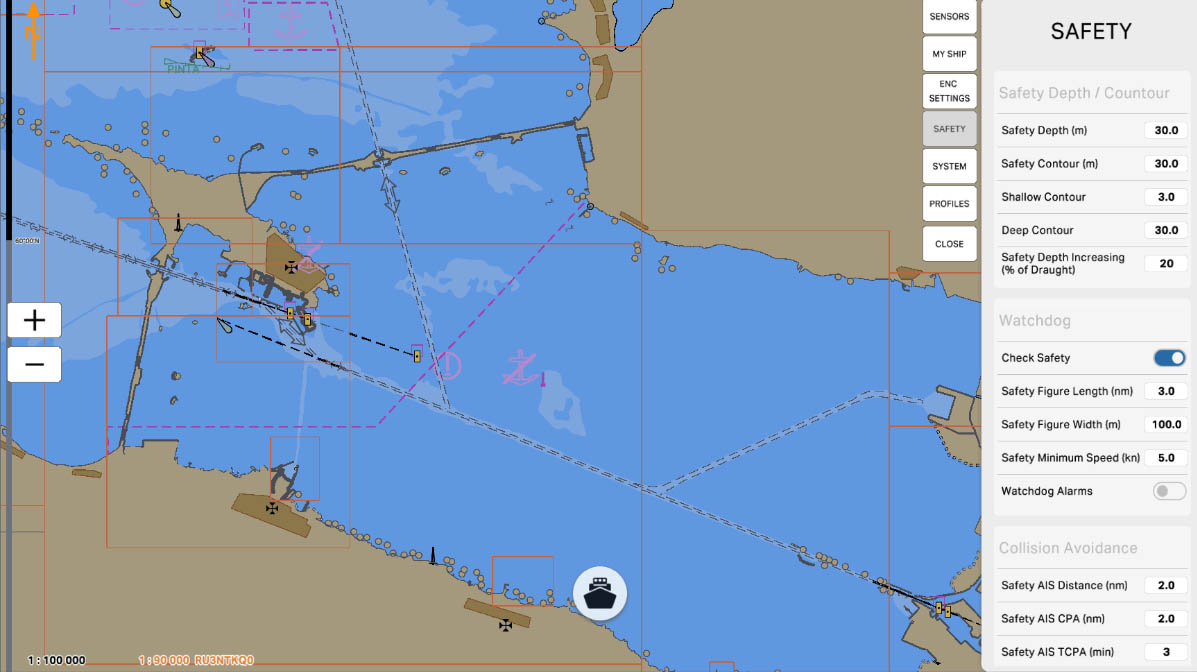
'Shallow Contour' is a setting that specifies a specific depth in meters, serving as a boundary to denote shallow waters on the nautical chart. This contour line visually marks the area where waters are considered shallow. Indicating shallow waters is crucial for mariners to avoid shallow areas and ensure navigation safety.
Safety Depth/Contour
7
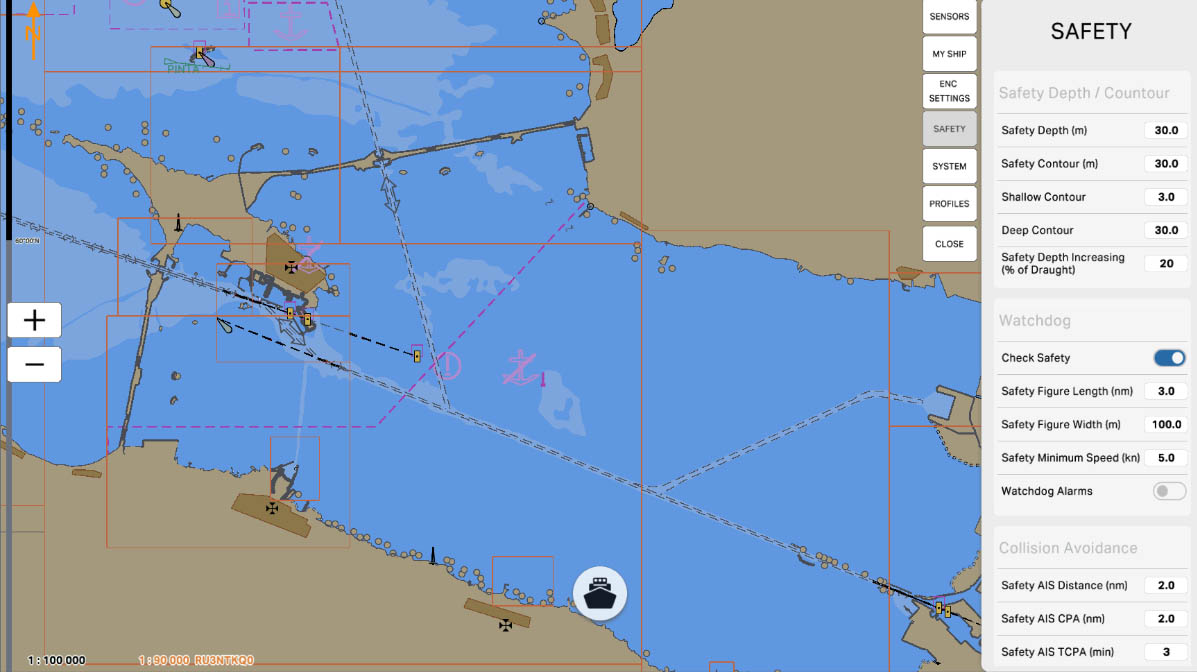
'Deep Contour' is a setting that defines a specific depth in meters, serving as the boundary for indicating deep waters on the nautical chart. This contour line visually marks the area where waters are considered deep. Specifying deep waters is crucial for mariners to avoid shallow areas and ensure navigational safety.
Safety Depth/Contour
8
The 'Safety Depth Increasing (% of Draught)' setting determines the increase in safety depth relative to the vessel's draft. This value specifies the percentage of the vessel's draft (the depth at which the vessel is considered safe) by which to increase the safety depth displayed on the nautical chart.
For example, if a vessel has a draft of 10 meters, and 'Safety Depth Increasing' is set to 20%, the system will automatically increase the safety depth by 20% of 10 meters, which would be an additional 2 meters. This is crucial for preventing potential hazards and ensuring safe navigation, taking into account the specifics of the vessel's draft.
For example, if a vessel has a draft of 10 meters, and 'Safety Depth Increasing' is set to 20%, the system will automatically increase the safety depth by 20% of 10 meters, which would be an additional 2 meters. This is crucial for preventing potential hazards and ensuring safe navigation, taking into account the specifics of the vessel's draft.
Safety Depth/Contour
9
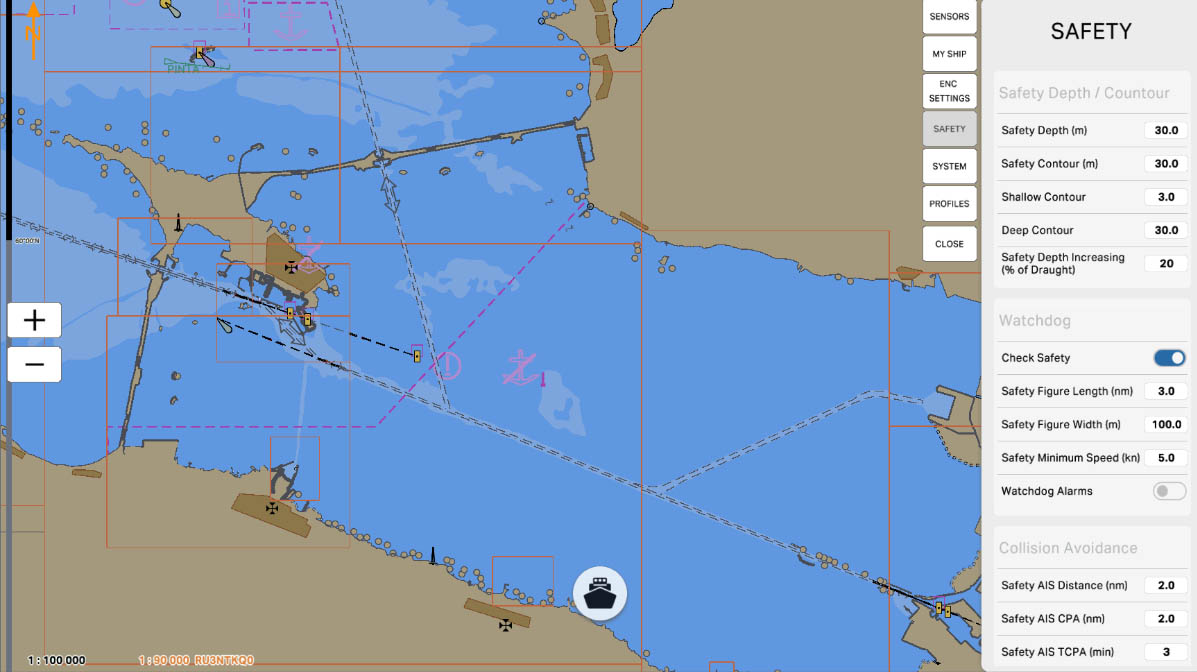
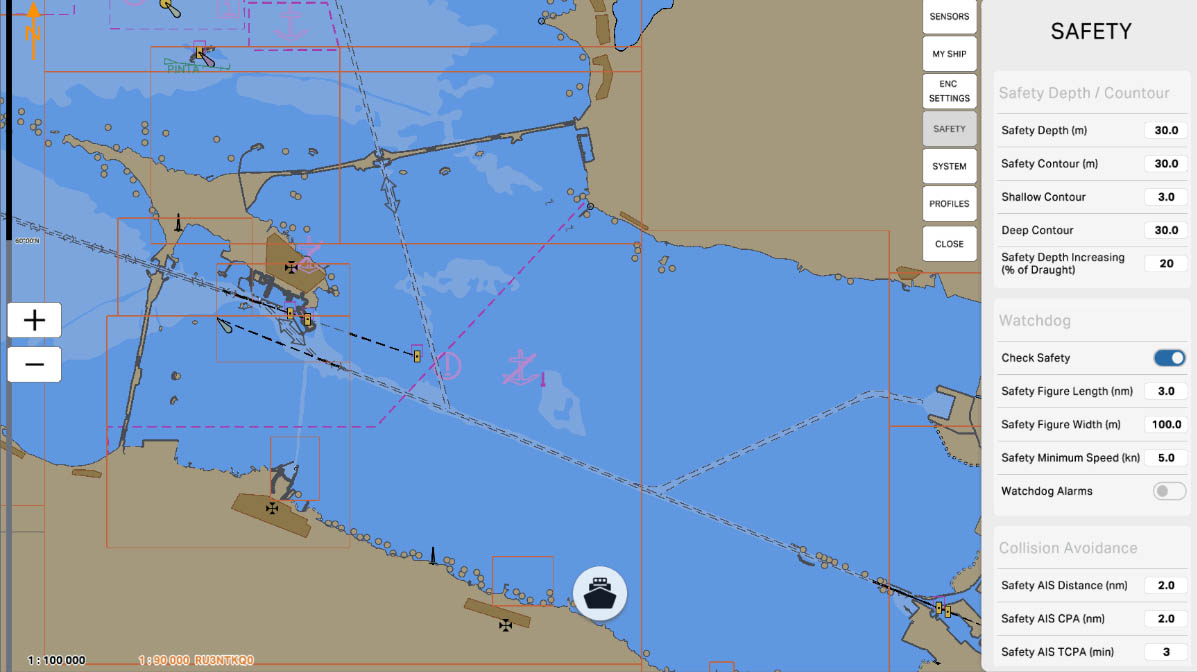
'Watchdog' is a function designed to monitor the operability of a system and promptly detect potential failures or malfunctions. This function may involve monitoring key components and system parameters, as well as providing warnings or automatic actions in case of issues.
The 'Watchdog' can be configured to identify abnormal situations, such as signal loss, malfunctions in components, or other anomalies, contributing to ensuring uninterrupted and safe system operation during navigation.
The 'Watchdog' can be configured to identify abnormal situations, such as signal loss, malfunctions in components, or other anomalies, contributing to ensuring uninterrupted and safe system operation during navigation.
SAFETY SETTINGS

10
The 'Check Safety' option is a feature that verifies the compliance of various aspects of the navigation system with established safety standards and parameters. This function may include monitoring key system components, the status of connected sensors, as well as checking for the availability of necessary updates for charts and software.
In case of potential violations or deviations from established standards, 'Check Safety' can warn the user, and in some cases, take automatic measures to restore the system's functionality and ensure safe navigation. This feature is aimed at maintaining a high level of reliability and safety of the system during operation.
In case of potential violations or deviations from established standards, 'Check Safety' can warn the user, and in some cases, take automatic measures to restore the system's functionality and ensure safe navigation. This feature is aimed at maintaining a high level of reliability and safety of the system during operation.
Watchdog
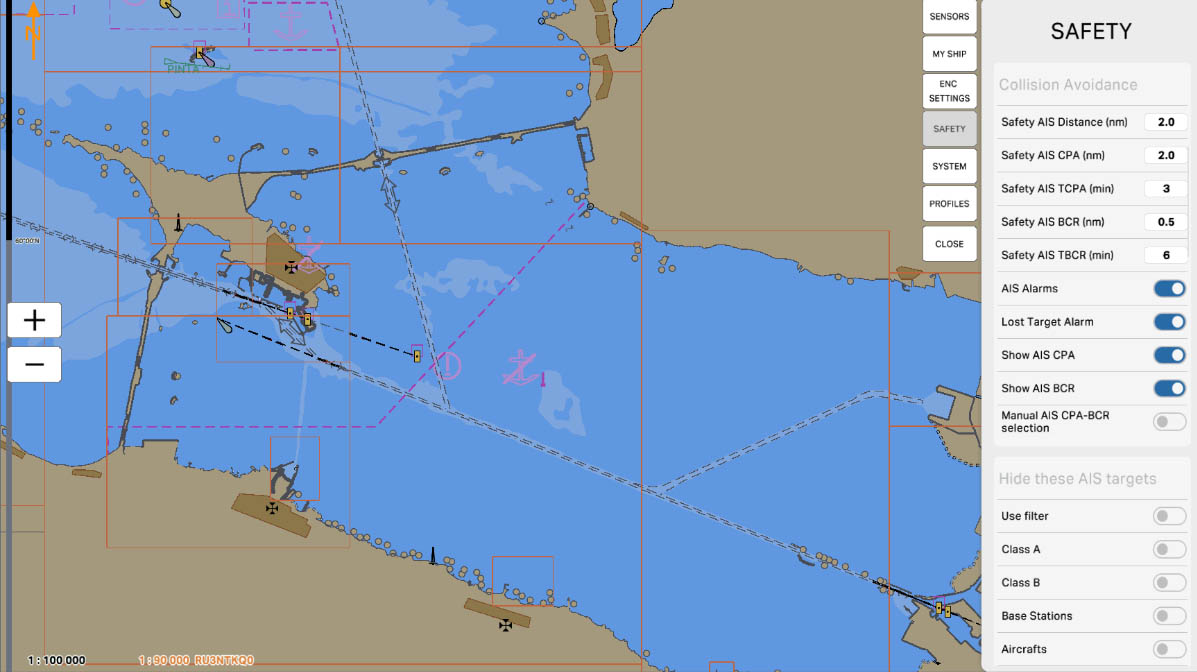
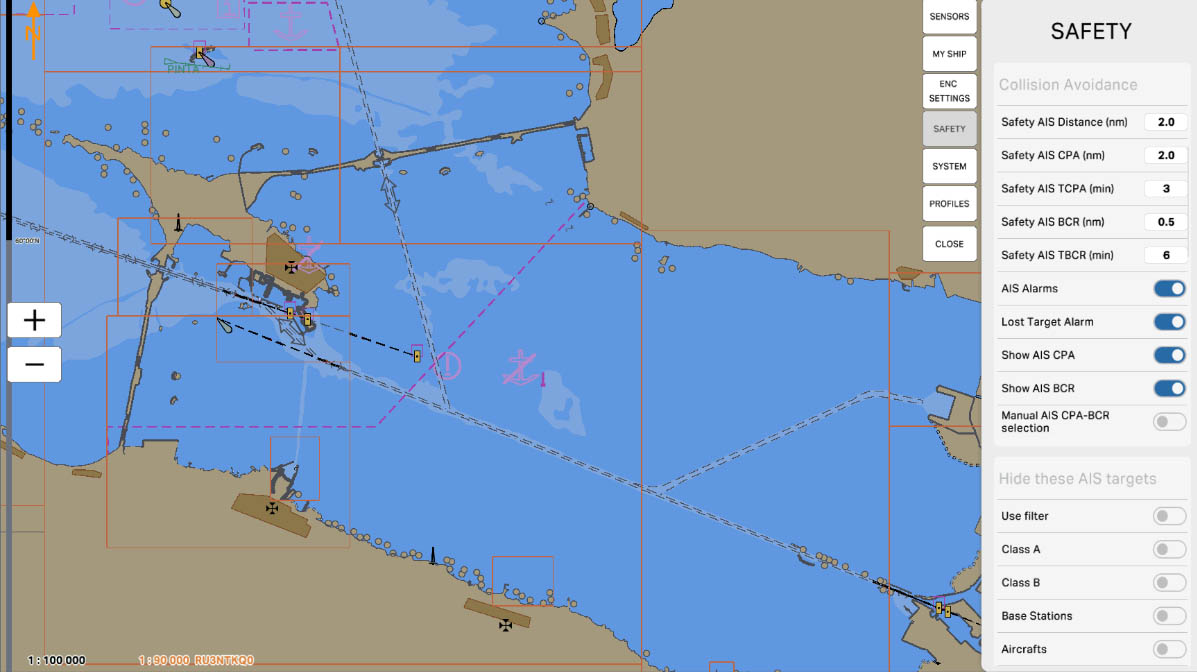
The 'Collision Avoidance' section pertains to parameters and settings related to preventing collisions with other objects during navigation. These settings may include defining areas where collisions are more likely, setting up warnings or automatic measures to prevent collisions, and other features aimed at ensuring the safety of vessels at sea.
SAFETY SETTINGS

15
16
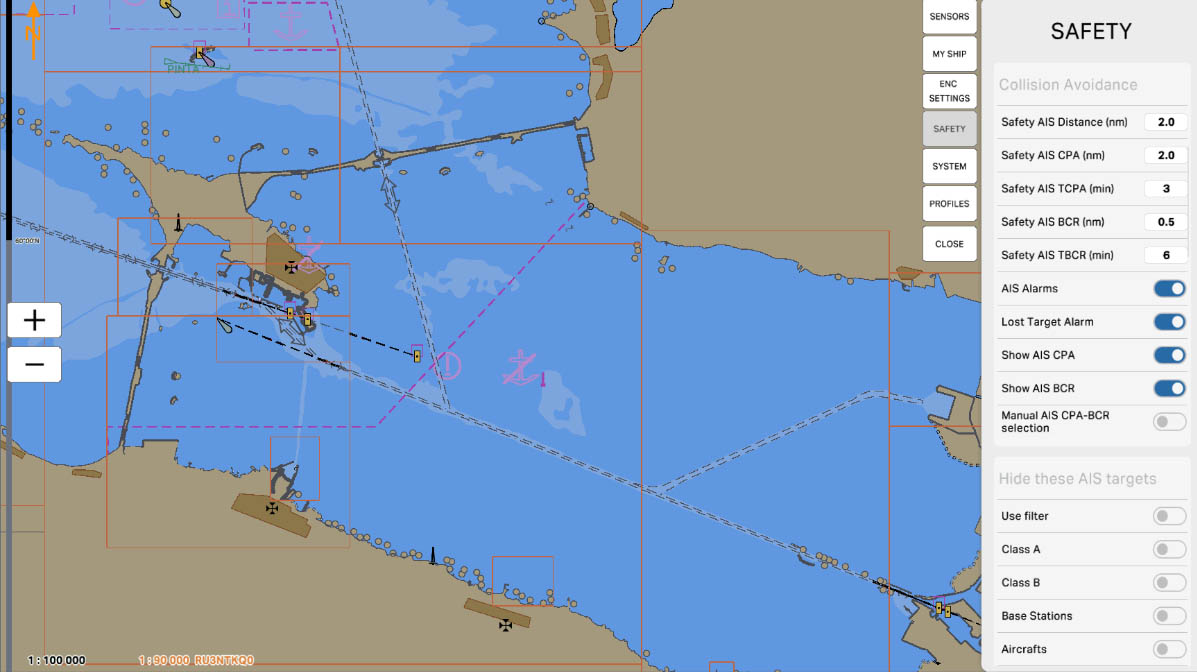
'Safety AIS Distance (nm)' is a parameter that defines the safe distance between your vessel and other vessels equipped with AIS (Automatic Identification System). AIS is used to exchange information about the location, course, speed, and other data between vessels to prevent collisions and ensure safe navigation.
The setting 'Safety AIS Distance' determines at what distance from your vessel the system will start warning about the potential danger of collision with other vessels, based on the data received from their AIS. This helps mariners take appropriate measures to prevent collisions and ensure safety at sea.
The setting 'Safety AIS Distance' determines at what distance from your vessel the system will start warning about the potential danger of collision with other vessels, based on the data received from their AIS. This helps mariners take appropriate measures to prevent collisions and ensure safety at sea.
Collision Avoidance
17
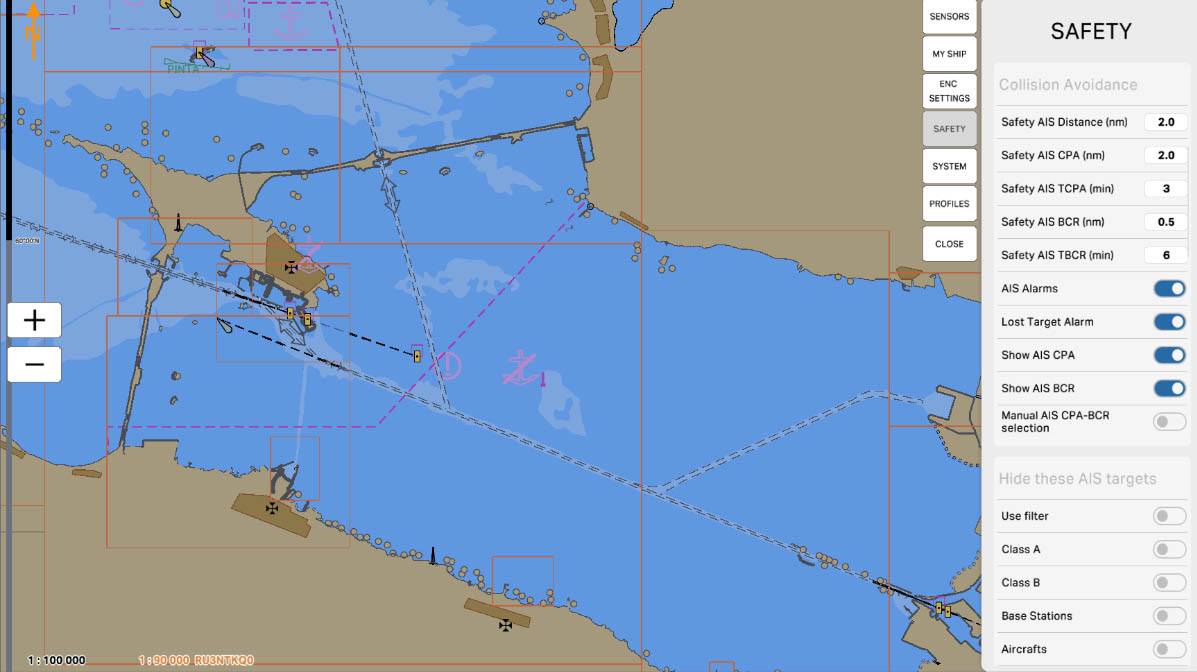
'Safety AIS CPA (nm)' sets the distance to the Closest Point of Approach (CPA) for collision prevention and safety using the Automatic Identification System (AIS).
The Closest Point of Approach (CPA) is the point at which two vessels have the minimum distance and the minimum horizontal relative course. This parameter, 'Safety AIS CPA', defines the safe distance between your vessel and other vessels using AIS data.
Configuring 'Safety AIS CPA' allows the system to warn mariners about close encounters with other vessels, helping to prevent collisions and ensuring safe navigation.
The Closest Point of Approach (CPA) is the point at which two vessels have the minimum distance and the minimum horizontal relative course. This parameter, 'Safety AIS CPA', defines the safe distance between your vessel and other vessels using AIS data.
Configuring 'Safety AIS CPA' allows the system to warn mariners about close encounters with other vessels, helping to prevent collisions and ensuring safe navigation.
Collision Avoidance
18
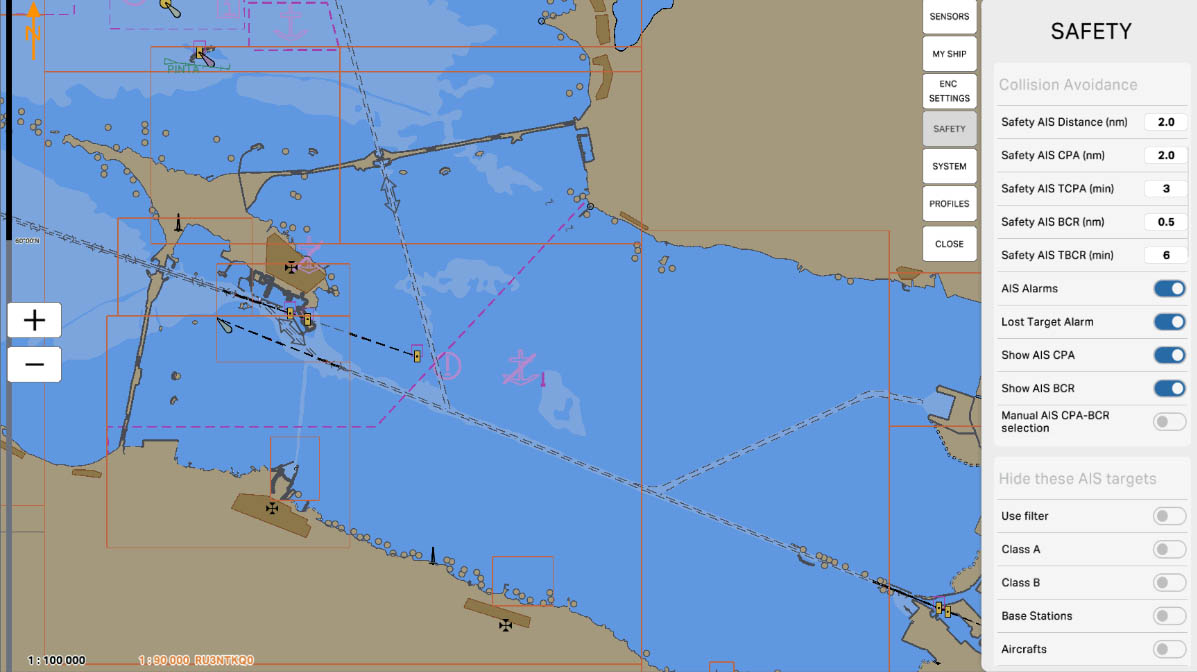
'Safety AIS TCPA (min)' sets the time to the nearest point of approach (TCPA) for collision avoidance and safety using the Automatic Identification System (AIS).
Time to the Nearest Point of Approach (TCPA) is the time interval, expressed in minutes, remaining until two vessels reach their closest point of approach. The 'Safety AIS TCPA' parameter determines a safe time for the system to alert about potential collision hazards with other vessels based on AIS data.
Configuring 'Safety AIS TCPA' allows the system to warn mariners about close approaches to other vessels, helping to prevent collisions and ensuring safe navigation.
Time to the Nearest Point of Approach (TCPA) is the time interval, expressed in minutes, remaining until two vessels reach their closest point of approach. The 'Safety AIS TCPA' parameter determines a safe time for the system to alert about potential collision hazards with other vessels based on AIS data.
Configuring 'Safety AIS TCPA' allows the system to warn mariners about close approaches to other vessels, helping to prevent collisions and ensuring safe navigation.
Collision Avoidance
19
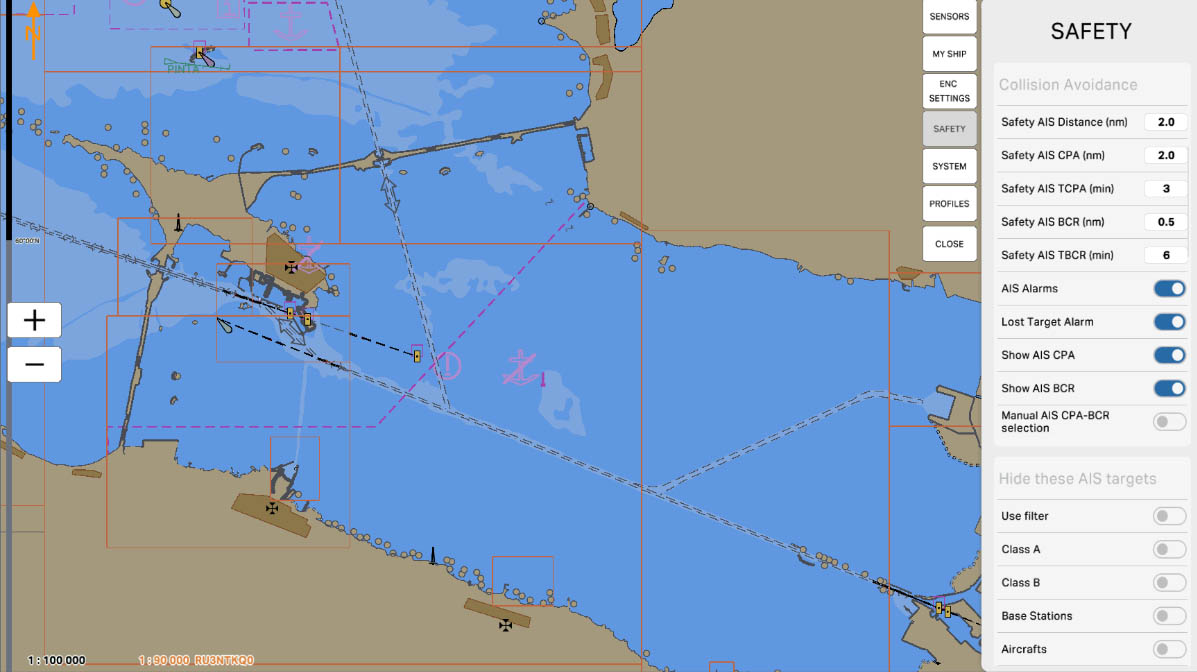
'Safety AIS BCR (nm)' is a parameter that sets the safe distance and orientation (bearing) between your vessel and other vessels equipped with AIS (Automatic Identification System) when it comes to bow crossing situations.
BCR, stands for 'Bow Crossing Range', which represents the distance between the bows of vessels. This parameter establishes criteria for the safe relative positioning in front of your vessel and other vessels to avoid collisions. It defines the safe distance, bearing, and rate of change of distance (if supported) between your vessel and other vessels using AIS data.
Configuring 'Safety AIS BCR' allows the system to provide warnings of potential collision hazards with other vessels and, if necessary, take actions to ensure safe navigation.
BCR, stands for 'Bow Crossing Range', which represents the distance between the bows of vessels. This parameter establishes criteria for the safe relative positioning in front of your vessel and other vessels to avoid collisions. It defines the safe distance, bearing, and rate of change of distance (if supported) between your vessel and other vessels using AIS data.
Configuring 'Safety AIS BCR' allows the system to provide warnings of potential collision hazards with other vessels and, if necessary, take actions to ensure safe navigation.
Collision Avoidance
20
'Safety AIS TBCR (min)' is a parameter that sets the safe time, in minutes, to the Bow Crossing Range (TBCR) between your vessel and other vessels equipped with AIS (Automatic Identification System).
TBCR stands for 'Time to Bow Crossing Range', representing the time remaining until the vessels cross each other's bows. This parameter determines the minimum safe time before the vessels' bows cross.
Configuring 'Safety AIS TBCR' allows the system to warn of potential collision hazards with other vessels ahead and, if necessary, take actions to ensure safe navigation.
TBCR stands for 'Time to Bow Crossing Range', representing the time remaining until the vessels cross each other's bows. This parameter determines the minimum safe time before the vessels' bows cross.
Configuring 'Safety AIS TBCR' allows the system to warn of potential collision hazards with other vessels ahead and, if necessary, take actions to ensure safe navigation.
Collision Avoidance
21
Enable the 'AIS Alarms' function to receive emergency signals or warnings related to AIS information. These warnings may include signals about proximity to other vessels, violation of safe distances, changes in the course or speed of other vessels, and other scenarios where AIS data indicates potential collision hazards.
Configuring 'AIS Alarms' allows users to determine which events related to AIS require warnings or emergency signals to ensure navigation safety and prevent collisions with other vessels.
Configuring 'AIS Alarms' allows users to determine which events related to AIS require warnings or emergency signals to ensure navigation safety and prevent collisions with other vessels.
Collision Avoidance
23
Enabling the 'Show AIS CPA' option allows displaying information about the Closest Point of Approach (CPA) for targets equipped with AIS (Automatic Identification System). The CPA is the nearest anticipated point where vessels could come closest in both space and time. This information is valuable for assessing potential collision hazards and taking measures to prevent collisions.
Collision Avoidance
24
Enabling the 'Show AIS BCR' option allows displaying information about Bow Crossing Range (BCR) for targets equipped with AIS (Automatic Identification System). BCR represents the distance between the bows of vessels as they encounter each other.
Showing BCR information is valuable for visually assessing the relative position and preventing collisions between vessels. The visual representation of this information on the screen helps mariners make informed decisions about the safe passage of other vessels.
Showing BCR information is valuable for visually assessing the relative position and preventing collisions between vessels. The visual representation of this information on the screen helps mariners make informed decisions about the safe passage of other vessels.
Collision Avoidance
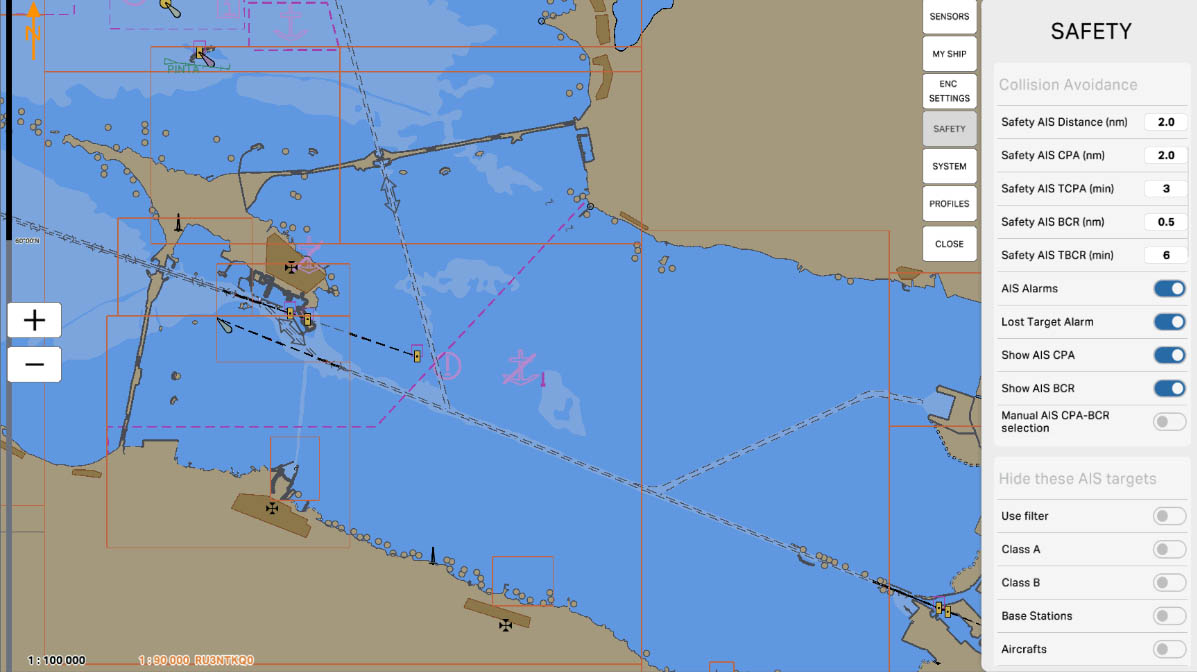
25
'Manual AIS CPA-BCR selection' is an option that allows the user to manually select the Closest Point of Approach (CPA) and Bow Crossing Range (BCR) values for targets equipped with AIS (Automatic Identification System).
When this option is enabled, the user can manually determine the CPA and BCR values for each target based on their movement and the anticipated mutual position. This provides an additional level of control and flexibility in managing collision avoidance parameters to ensure navigation safety.
When this option is enabled, the user can manually determine the CPA and BCR values for each target based on their movement and the anticipated mutual position. This provides an additional level of control and flexibility in managing collision avoidance parameters to ensure navigation safety.
Collision Avoidance
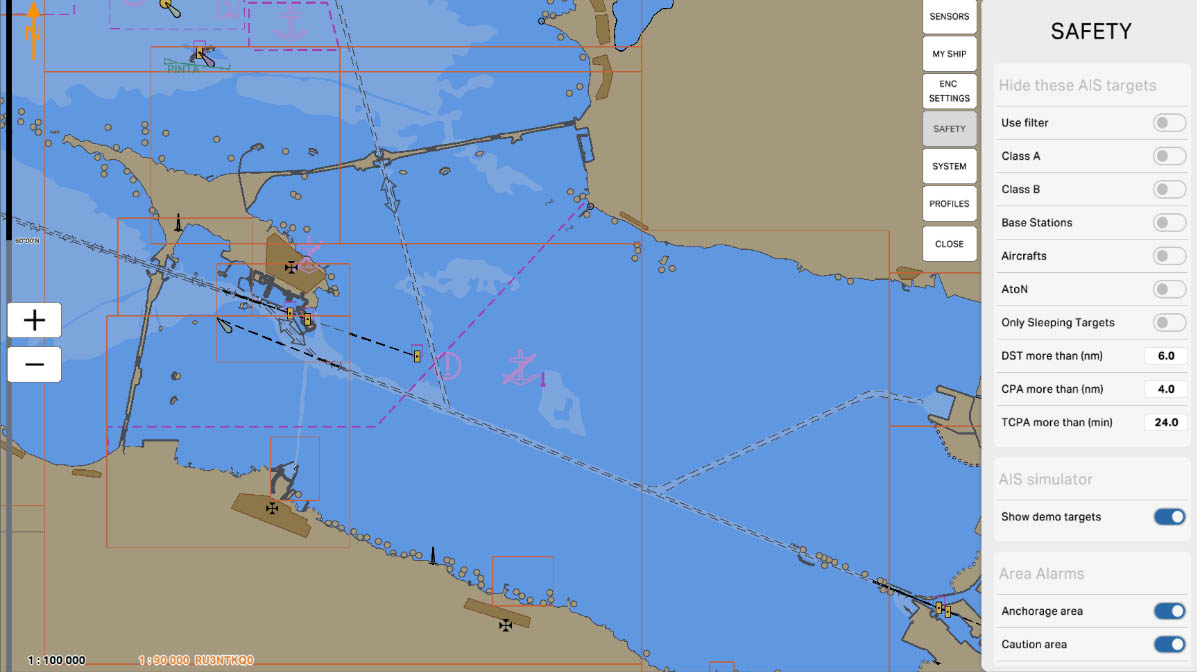
28
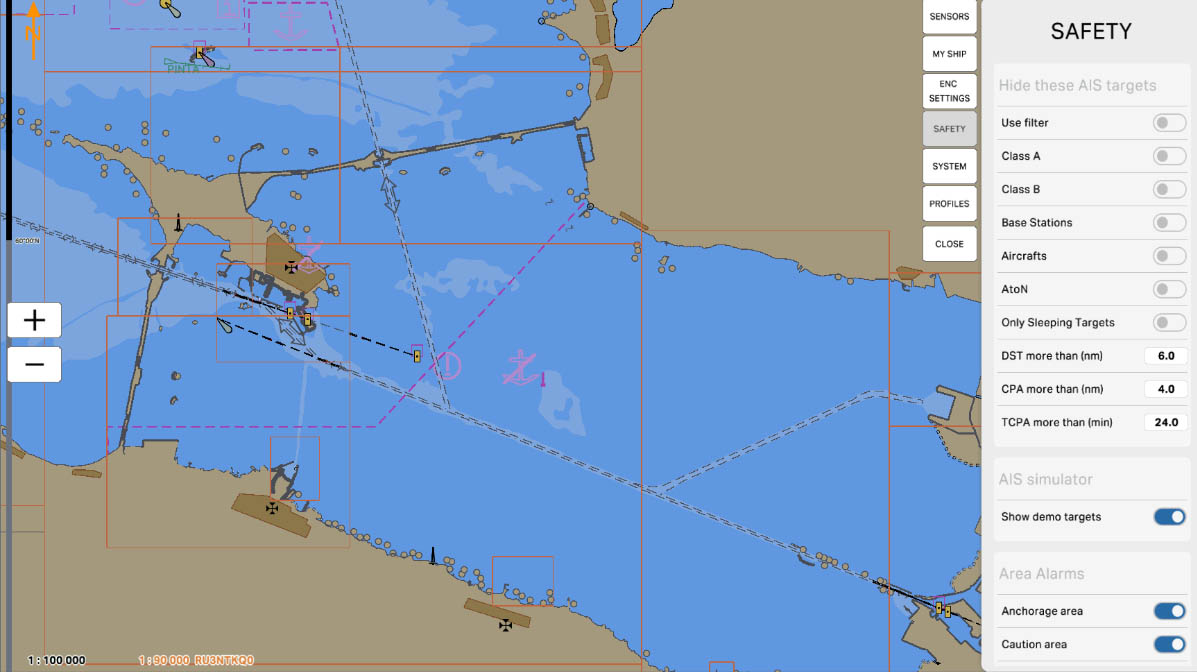
The "Class A" option is designed to manage the display of vessels equipped with Class A AIS transponders. These transponders are installed on large commercial vessels such as container ships, tankers, and passenger liners, providing detailed information about the vessel's position, course, speed, and other important parameters. Enabling this option allows you to hide such vessels on the screen, which can be useful for reducing visual clutter on the map in high-traffic conditions.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
29
The "Class B" option is designed to manage the display of vessels equipped with Class B AIS transponders. These transponders are installed on smaller commercial and private vessels such as yachts, fishing boats, and small cargo ships. Enabling this option allows you to hide such vessels on the screen, helping to reduce visual clutter on the map and focus on larger and potentially more significant vessels.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
30
The "Base Stations" option is designed to manage the display of AIS base stations on the map. Base stations are used for monitoring and managing maritime traffic, as well as for transmitting data between vessels and shore services. Enabling this option allows you to hide base stations on the screen, which can be useful for simplifying the visualization of the navigational environment and focusing on moving objects.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
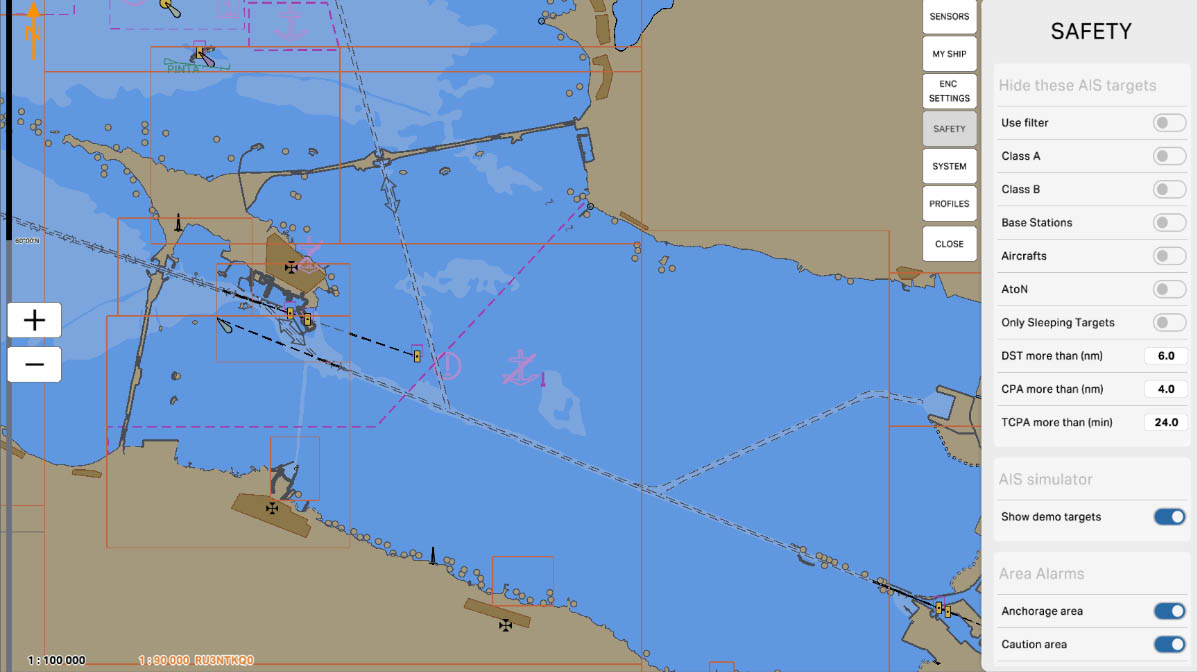
31
The "Aircrafts" option is designed to manage the display of aircraft equipped with AIS on the map. Aircraft may be equipped with AIS to enhance situational awareness and prevent collisions. Enabling this option allows you to hide aircraft on the screen, which can be useful if the main focus is required on maritime objects.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
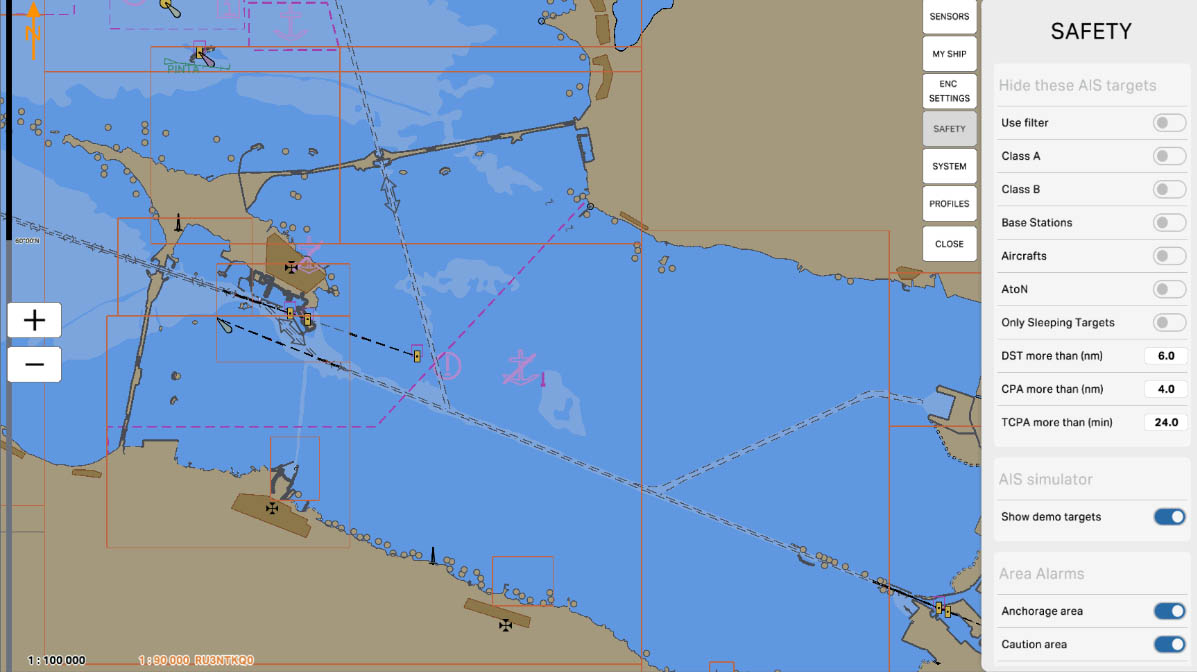
32
The "AtoN" (Aid to Navigation) option is designed to manage the display of navigation aids equipped with AIS on the map. Navigation aids, such as lighthouses, buoys, and beacons, may be equipped with AIS to transmit their position and status. Enabling this option allows you to hide these navigation objects on the screen, which can be useful for simplifying the display and reducing visual clutter on the map.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
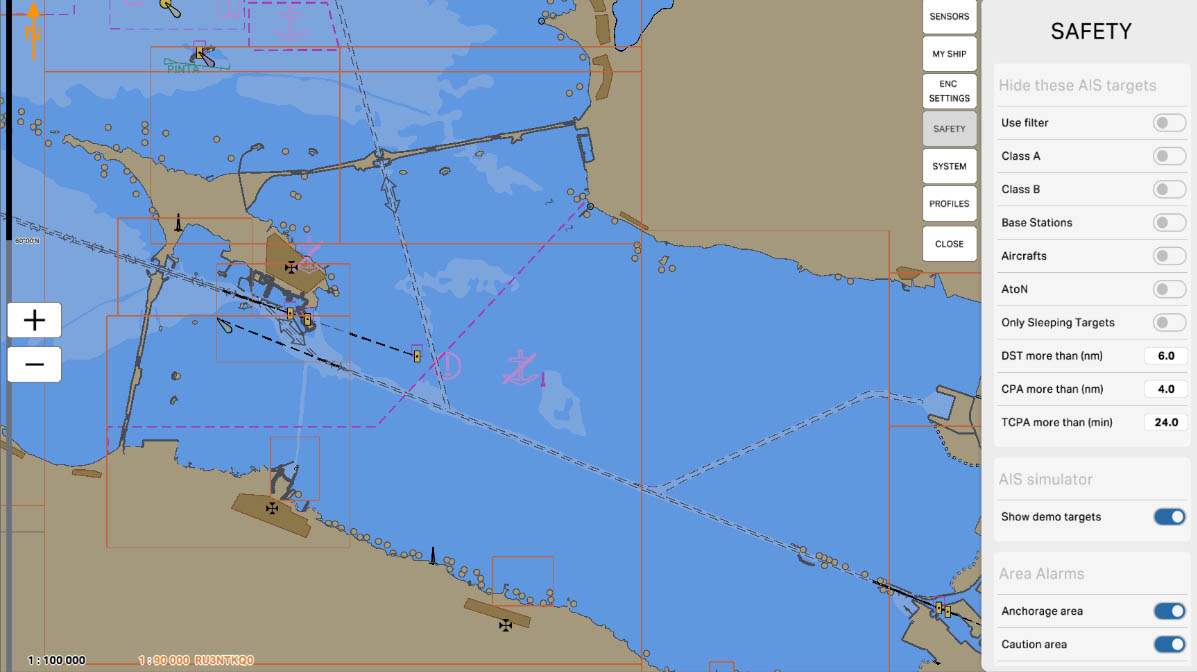
33
The "Only Sleeping Targets" option is designed to manage the display of AIS targets on the map that are in a "sleeping" state. Sleeping targets are those objects that are transmitting their data but do not pose an immediate threat or interest, meaning they do not require immediate action from the operator.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
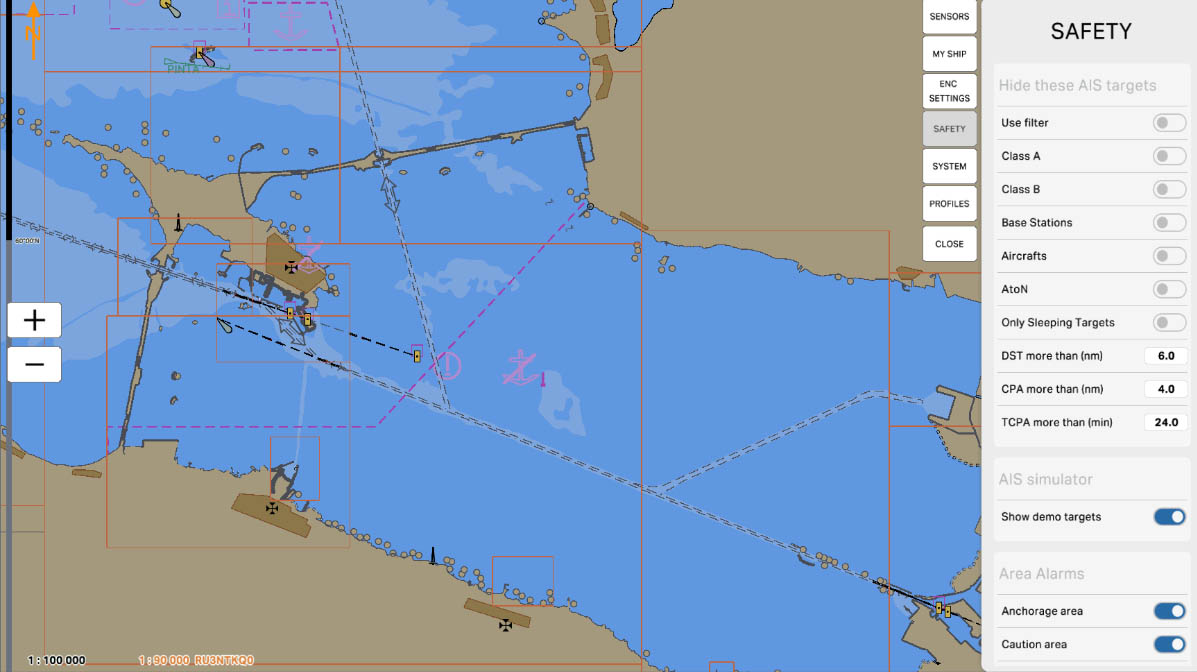
34
The "DST more than (nm)" parameter is used to filter AIS targets by distance. It allows you to hide all targets on the map that are located beyond the specified distance in nautical miles (nm). This is useful for reducing visual clutter and focusing on closer and potentially more important targets that require the operator's attention.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
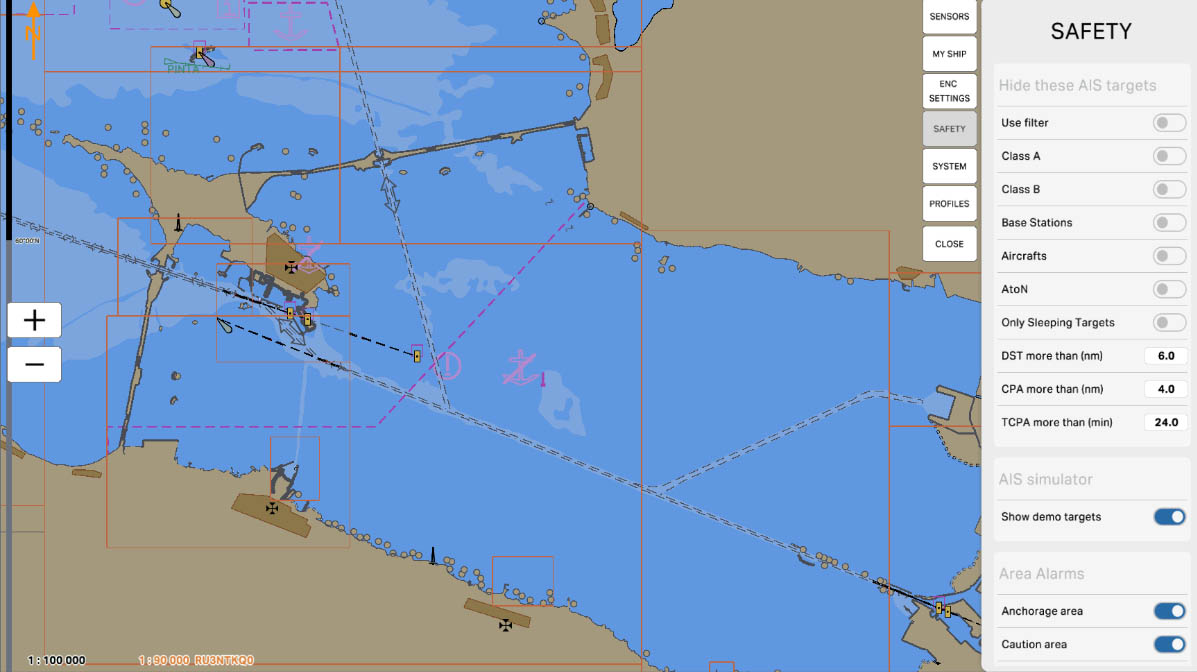
35
The "CPA more than (nm)" parameter is used to filter AIS targets based on their Closest Point of Approach (CPA) value. This parameter allows you to hide all targets on the map whose CPA value exceeds the specified number of nautical miles (nm). This helps operators focus on targets that pose a potential collision threat and are in close proximity to your vessel.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
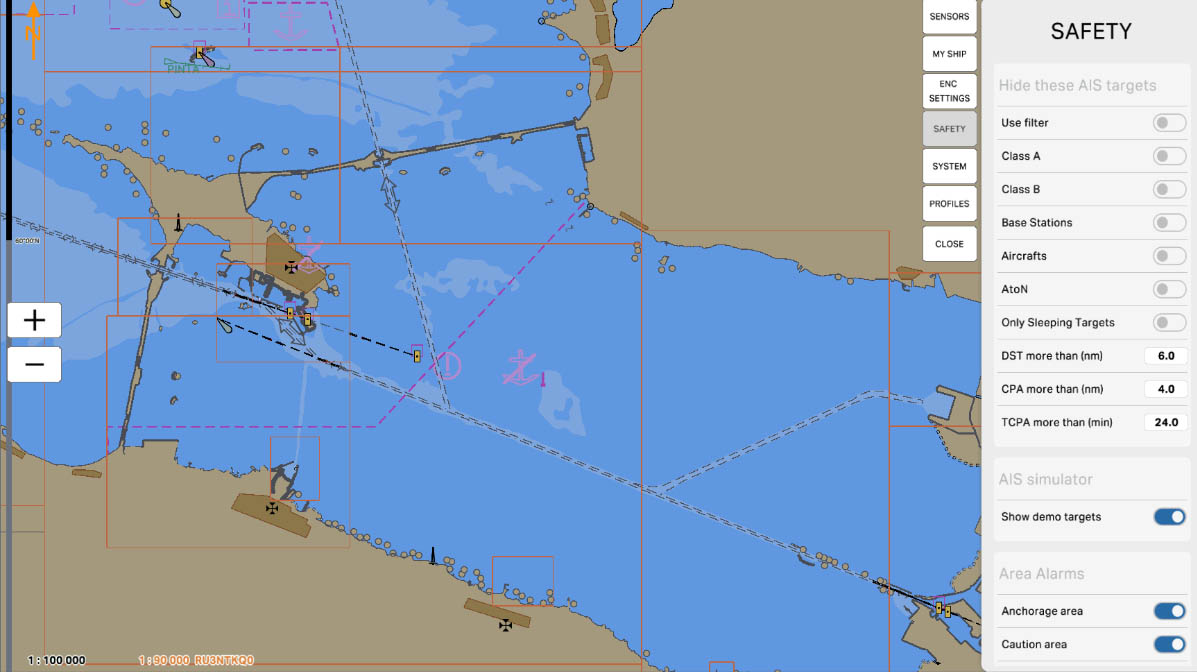
36
The "TCPA more than (min)" parameter is used to filter AIS targets based on their Time to Closest Point of Approach (TCPA) value. This parameter allows you to hide all targets on the map whose TCPA value exceeds the specified number of minutes. This helps operators focus on targets that are approaching your vessel in the near future and may pose a collision threat.
AIS Drawing Filtering - hiding targets
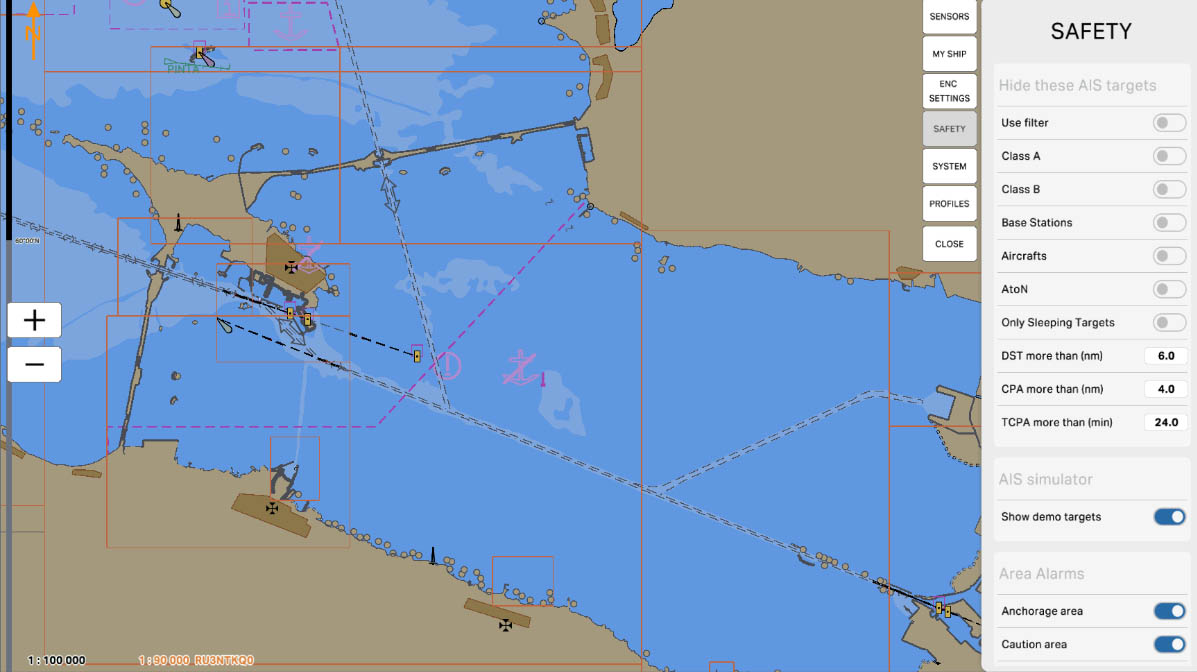
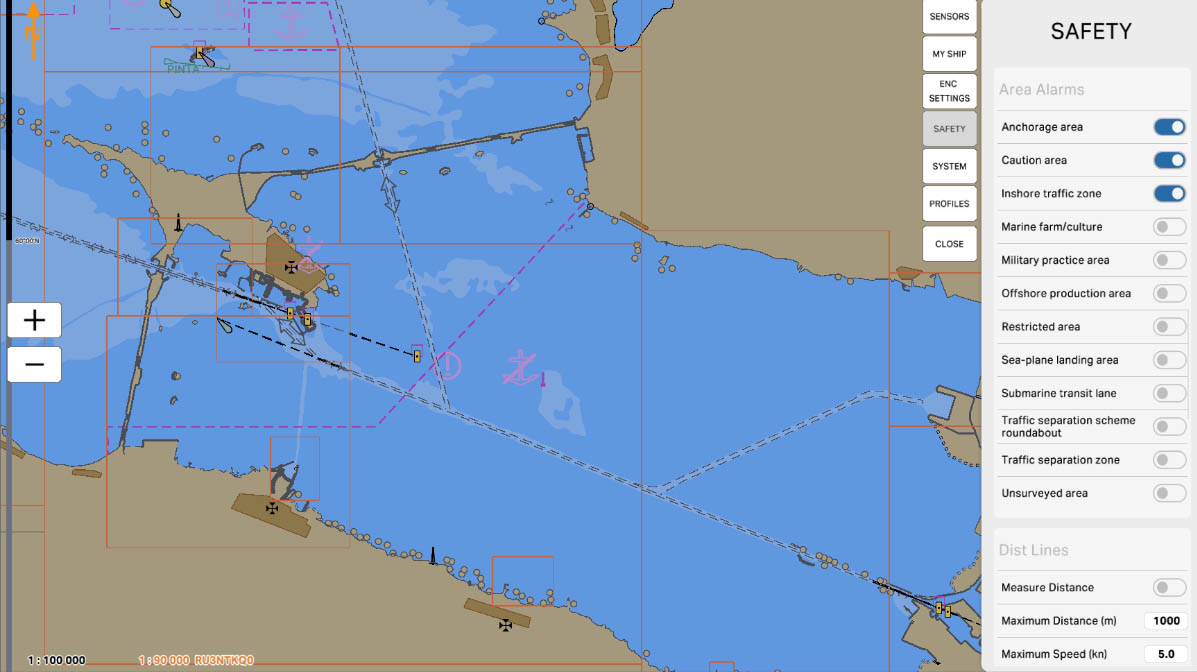
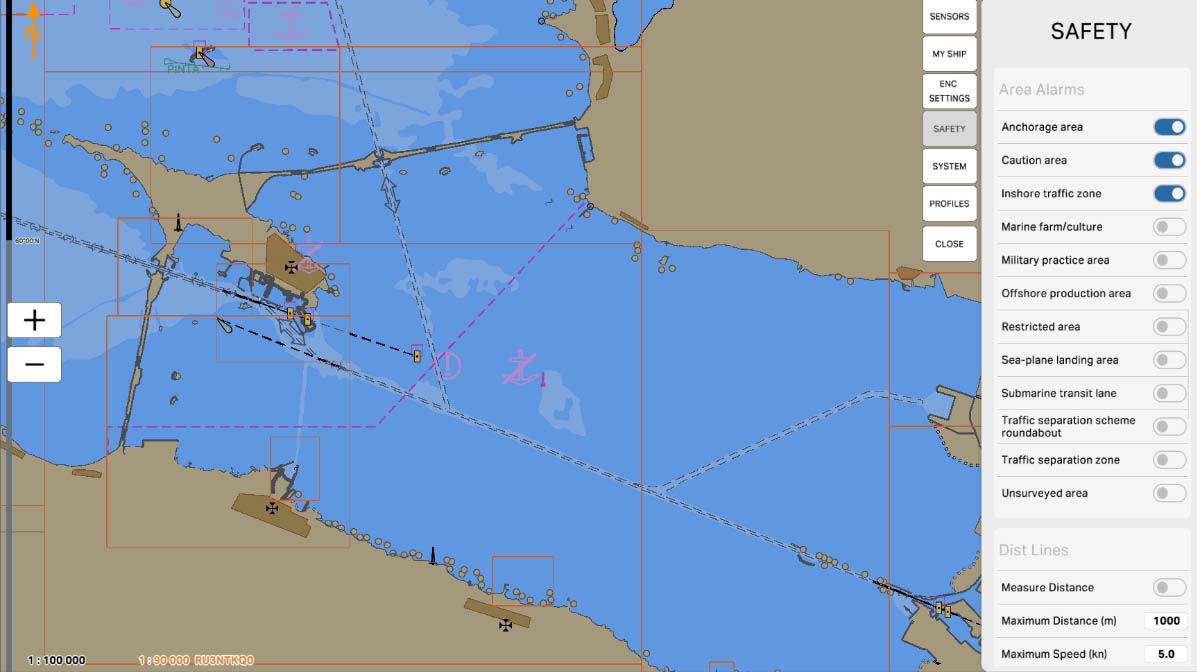
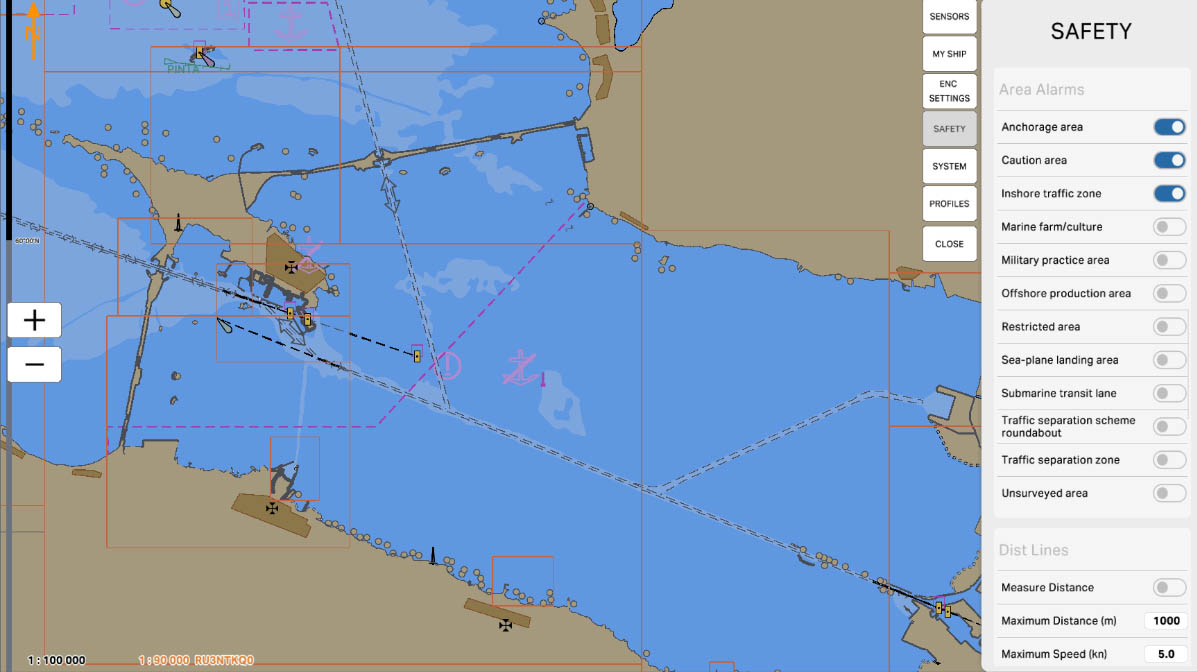
The 'Area Alarms' section in safety settings contains options and parameters related to setting up warnings and alarms for specific areas on the nautical chart. These settings may include defining hazardous or restricted zones, marking boundaries of specific water areas, and setting up warnings for entry into certain maritime regions.
SAFETY SETTINGS

38
39
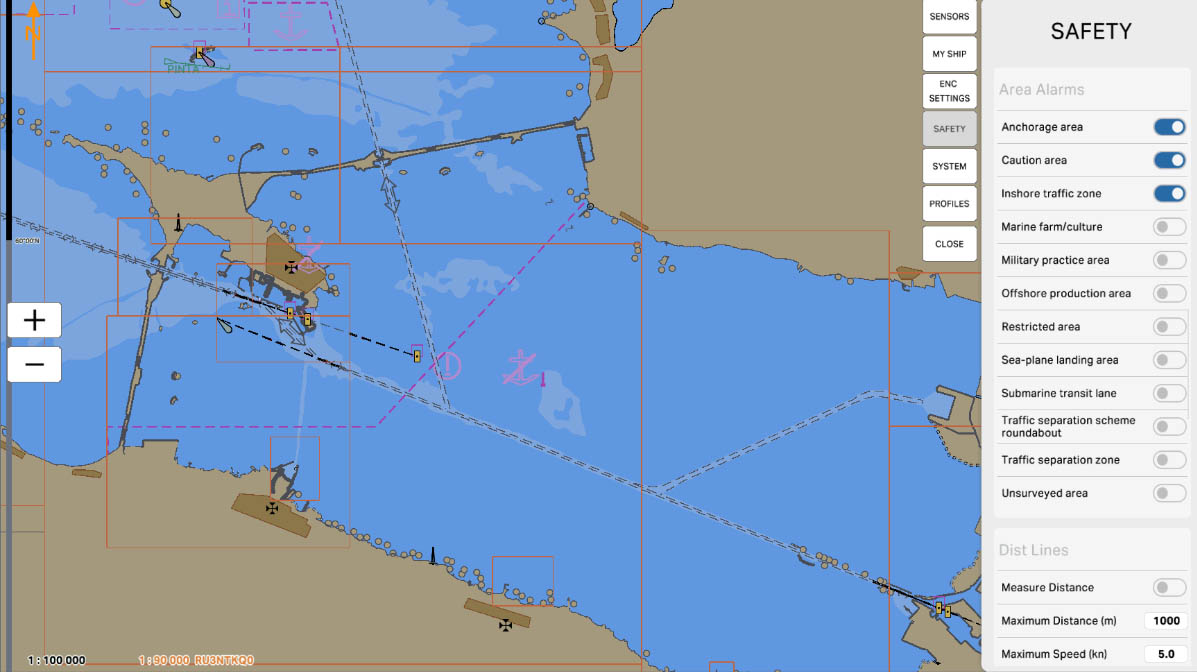
Enable the 'Anchorage Area' option to receive warnings and alarms for sea areas designated for maritime anchoring. These settings alert mariners against entering areas where vessels may be anchored, crucial for avoiding potential collisions and ensuring navigation safety.
Area Alarms
40
'Caution Area' refers to zones on the nautical chart for which warnings and alarms are configured. These settings alert mariners against entering specific areas where special conditions or potential hazards exist, requiring extra caution.
'Caution Area' may be applied, for example, to highlight regions with limited visibility, the presence of underwater obstacles, or other particular conditions that could impact navigation safety. This feature helps mariners avoid potential risks and ensures safety when navigating close to specific areas on the nautical chart.
'Caution Area' may be applied, for example, to highlight regions with limited visibility, the presence of underwater obstacles, or other particular conditions that could impact navigation safety. This feature helps mariners avoid potential risks and ensures safety when navigating close to specific areas on the nautical chart.
Area Alarms
41
'Inshore Traffic Zone' refers to zones on the nautical chart where warnings and alarms are set for inshore traffic areas. These zones delineate areas close to the shore where vessel traffic can be intense, and specific rules and safety measures apply.
Configuring the 'Inshore Traffic Zone' alerts mariners about approaching coastal traffic zones and reminds them to adhere to specific rules established for these areas. This is crucial for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in coastal waters.
Configuring the 'Inshore Traffic Zone' alerts mariners about approaching coastal traffic zones and reminds them to adhere to specific rules established for these areas. This is crucial for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in coastal waters.
Area Alarms
42
'Marine Farm/Culture' refers to zones on the nautical chart where warnings and alarms are set related to aquaculture or marine farms. These areas may include aquaculture sites where the cultivation of marine products such as fish, mussels, or seaweed takes place.
Enabling the 'Marine Farm/Culture' option alerts mariners to the presence of aquaculture zones and may provide information that movement in these areas could be restricted or that special rules are in place to ensure safety and prevent damage to marine farms. This is important to avoid potential collisions and comply with regulations in these areas.
Enabling the 'Marine Farm/Culture' option alerts mariners to the presence of aquaculture zones and may provide information that movement in these areas could be restricted or that special rules are in place to ensure safety and prevent damage to marine farms. This is important to avoid potential collisions and comply with regulations in these areas.
Area Alarms
43
'Military Practice Area' is a zone on the maritime chart where warnings and alarms related to military exercises or practice are configured. These areas may be used by military forces for training, shooting exercises, and other military activities.
Configuring the 'Military Practice Area' setting alerts mariners to the presence of military practice zones and may include information indicating potential threats to navigation or the use of military assets, requiring special caution. This is crucial for ensuring safety and preventing vessels from entering areas designated for military exercises.
Configuring the 'Military Practice Area' setting alerts mariners to the presence of military practice zones and may include information indicating potential threats to navigation or the use of military assets, requiring special caution. This is crucial for ensuring safety and preventing vessels from entering areas designated for military exercises.
Area Alarms
44
'Offshore Production Area' — these are zones on the maritime chart where warnings and alarms are set regarding areas of offshore production, such as offshore oil and gas platforms. These areas represent locations for extracting resources from the sea.
Configuring the 'Offshore Production Area' warns mariners about the presence of offshore production zones and may include information that these areas might have intense maritime traffic, along with special rules and safety measures. This is crucial for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in the surrounding waters.
Configuring the 'Offshore Production Area' warns mariners about the presence of offshore production zones and may include information that these areas might have intense maritime traffic, along with special rules and safety measures. This is crucial for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in the surrounding waters.
Area Alarms
45
'Restricted Area' is an area on the nautical chart where warnings and alarms are set. In these areas, there are restrictions that can range from prohibitions on entering specific locations to additional safety measures that mariners must adhere to.
Enabling the 'Restricted Area' setting alerts mariners to the presence of zones with restrictions and may include information about additional rules, movement limitations, or other conditions that could affect the safety of navigation in these areas. This is crucial for preventing rule violations and ensuring the safety of vessels in restricted maritime zones.
Enabling the 'Restricted Area' setting alerts mariners to the presence of zones with restrictions and may include information about additional rules, movement limitations, or other conditions that could affect the safety of navigation in these areas. This is crucial for preventing rule violations and ensuring the safety of vessels in restricted maritime zones.
Area Alarms
46
'Sea-plane Landing Area' — these are zones for which warnings and alarms are set on the maritime chart, related to areas designated for the landing of seaplanes. These areas are designed for the takeoff and landing of seaplanes.
Enabling the 'Sea-plane Landing Area' option alerts mariners to the presence of seaplane landing zones and may include information that these areas may have intensive seaplane traffic, as well as special rules and safety measures. This is important for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in the surrounding waters.
Enabling the 'Sea-plane Landing Area' option alerts mariners to the presence of seaplane landing zones and may include information that these areas may have intensive seaplane traffic, as well as special rules and safety measures. This is important for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in the surrounding waters.
Area Alarms
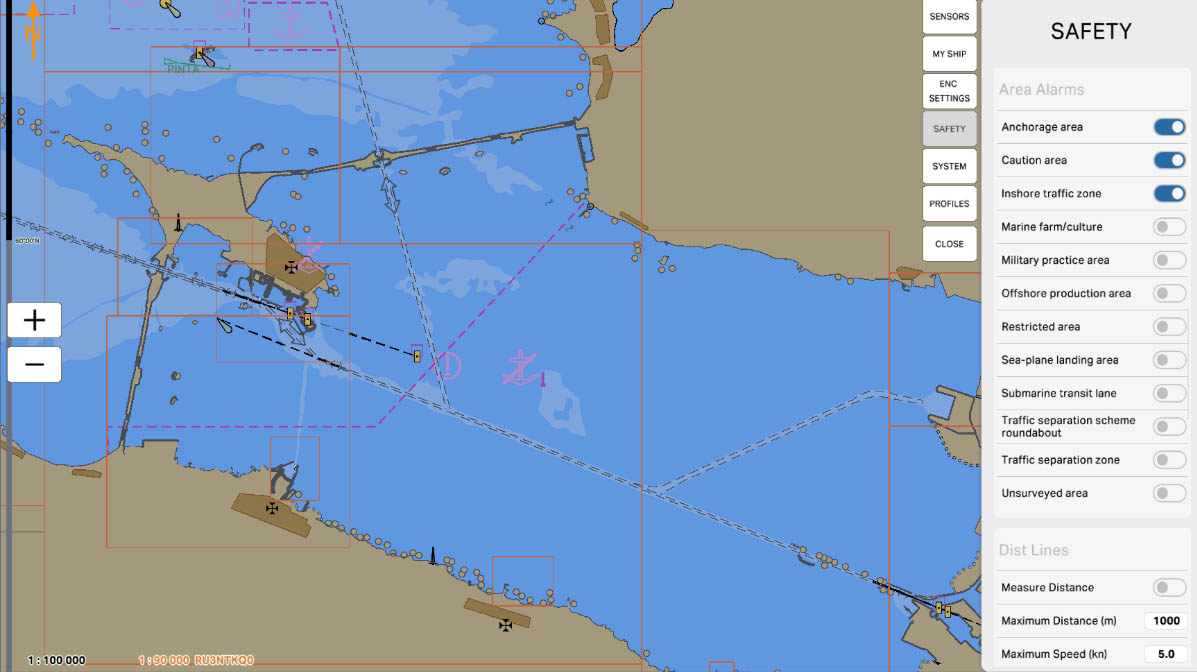
47
'Submarine Transit Lane' is an area on a nautical chart where warnings and alarms are set regarding the routes of submarines. These areas represent sections of the sea through which submarine routes may pass.
The 'Submarine Transit Lane' setting alerts mariners to the presence of zones for submarines and may include information that these areas may experience intense submarine traffic. Special rules and safety measures may apply in these zones. This is important for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in the surrounding waters.
The 'Submarine Transit Lane' setting alerts mariners to the presence of zones for submarines and may include information that these areas may experience intense submarine traffic. Special rules and safety measures may apply in these zones. This is important for preventing collisions, ensuring safety, and complying with regulations in the surrounding waters.
Area Alarms
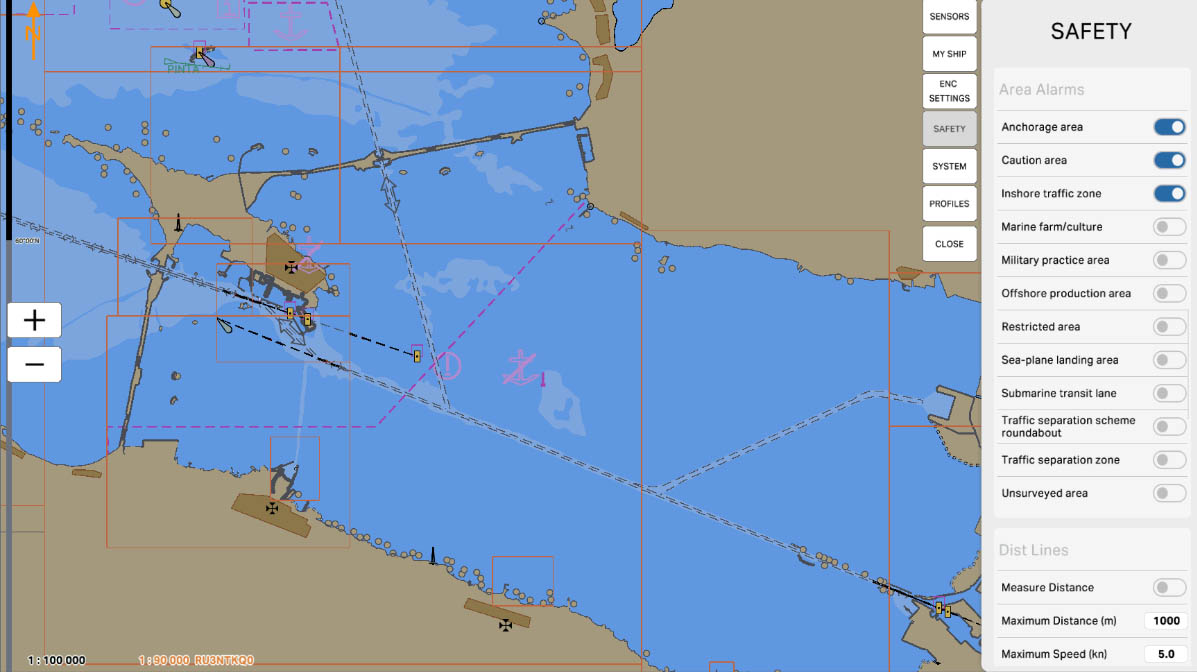
48
'Traffic Separation Scheme Roundabout' refers to areas on a nautical chart where warnings and alarms are set regarding circular segments within traffic separation schemes. These segments represent circular areas within traffic separation schemes where vessels are required to adhere to specific rules and follow a certain order of movement.
The 'Traffic Separation Scheme Roundabout' setting alerts mariners to the presence of circular segments within traffic separation schemes and reminds them to observe the rules and safety measures when navigating through these areas. This is important for preventing collisions, ensuring efficient vessel movement, and complying with regulations in these maritime zones.
The 'Traffic Separation Scheme Roundabout' setting alerts mariners to the presence of circular segments within traffic separation schemes and reminds them to observe the rules and safety measures when navigating through these areas. This is important for preventing collisions, ensuring efficient vessel movement, and complying with regulations in these maritime zones.
Area Alarms
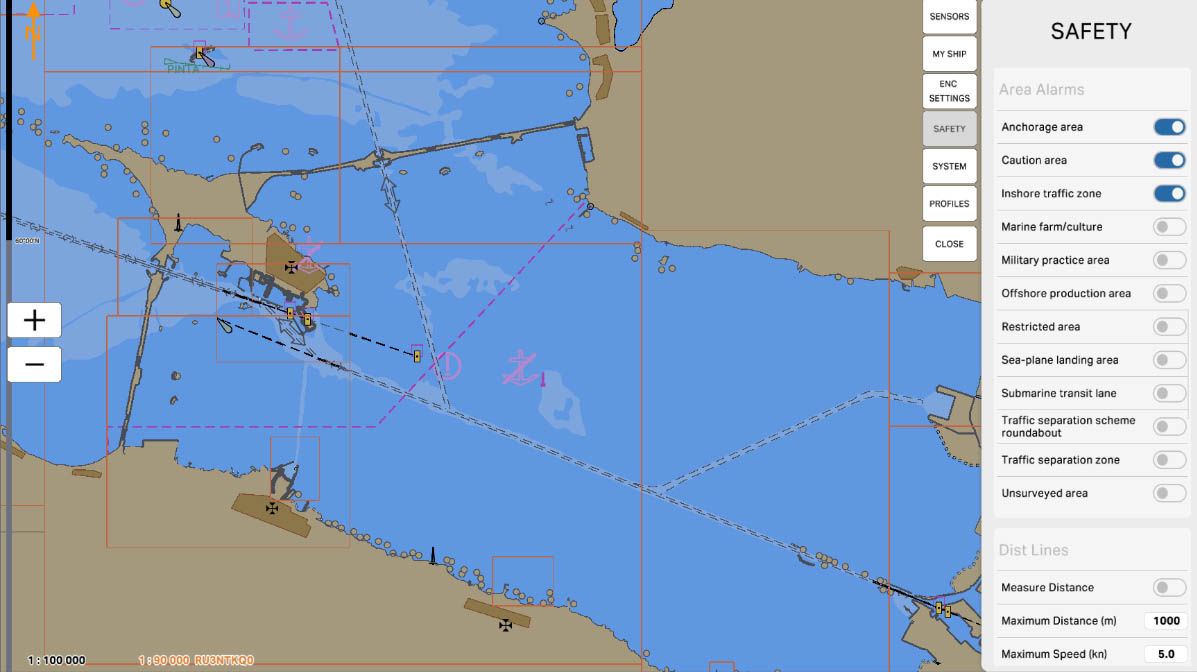
49
'Traffic Separation Zone' is an area on the maritime chart for which warnings and alarms are set in connection with traffic separation zones. These zones represent sections of the sea where vessel traffic is organized to prevent collisions. In traffic separation zones, vessels follow specific rules, such as being separated into two traffic flows with clearly defined directions.
Configuring the 'Traffic Separation Zone' alerts mariners to the presence of traffic separation zones and reminds them to adhere to rules and safety measures when navigating through these areas. This is crucial for preventing collisions, ensuring efficient vessel movement, and complying with regulations in these maritime zones.
Configuring the 'Traffic Separation Zone' alerts mariners to the presence of traffic separation zones and reminds them to adhere to rules and safety measures when navigating through these areas. This is crucial for preventing collisions, ensuring efficient vessel movement, and complying with regulations in these maritime zones.
Area Alarms
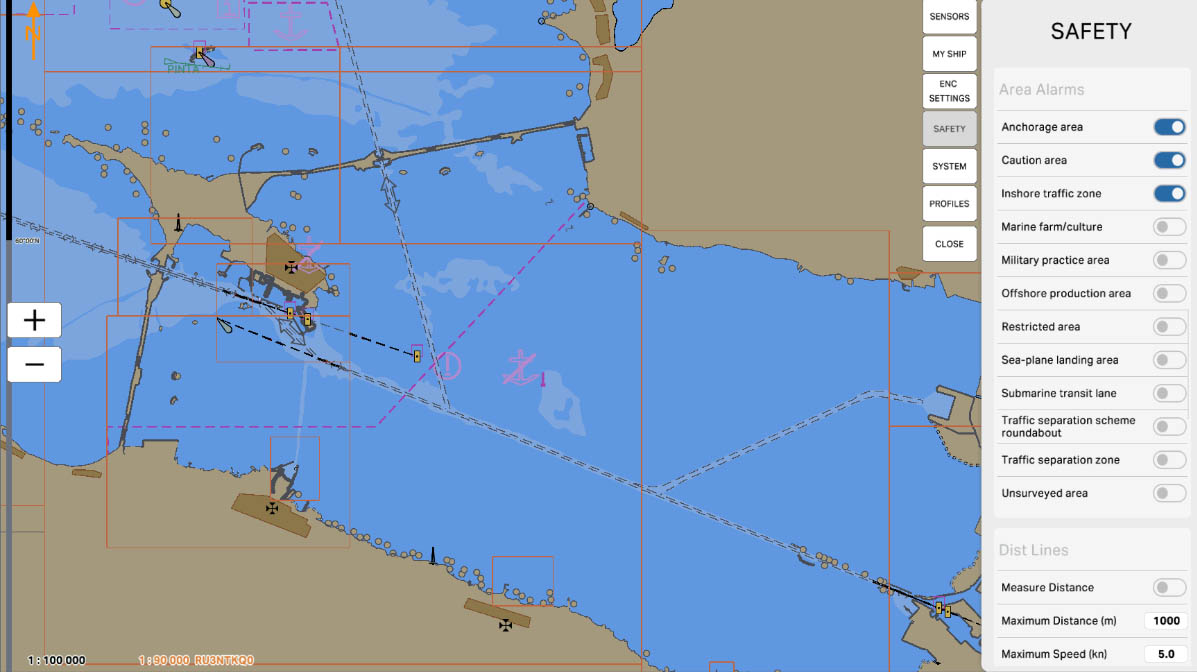
50
'Unsurveyed Area' — these are zones for which warnings and alarms are set on the nautical chart, related to areas that have not been thoroughly surveyed or verified. These areas may lack detailed hydrographic information or official survey data.
The 'Unsurveyed Area' setting alerts mariners to the presence of areas where reliable data may be lacking, emphasizing the need for caution when navigating in these regions. This is crucial for ensuring safety and avoiding potential unforeseen situations at sea.
The 'Unsurveyed Area' setting alerts mariners to the presence of areas where reliable data may be lacking, emphasizing the need for caution when navigating in these regions. This is crucial for ensuring safety and avoiding potential unforeseen situations at sea.
Area Alarms
54
'Maximum Speed (kn)' - this option is related to speed measurement. The user can set the maximum speed in knots that can be used when measuring time for distance calculation. If the set speed exceeds this value, the system may provide a warning or limit the ability to conduct measurements.
Distance Lines
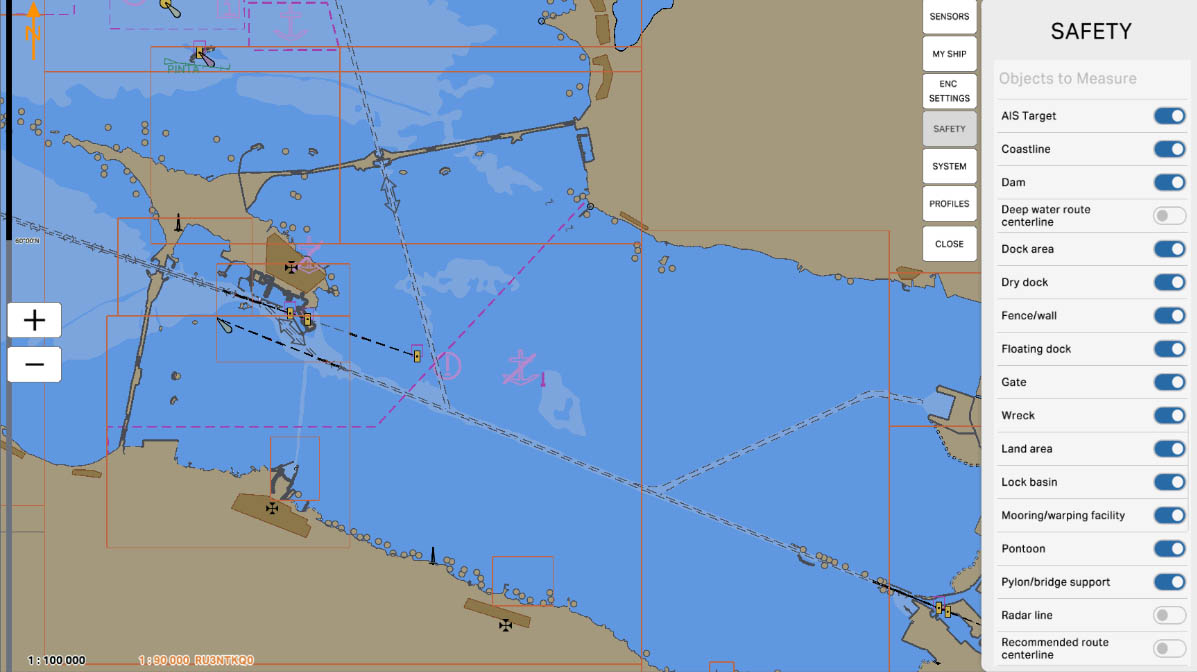
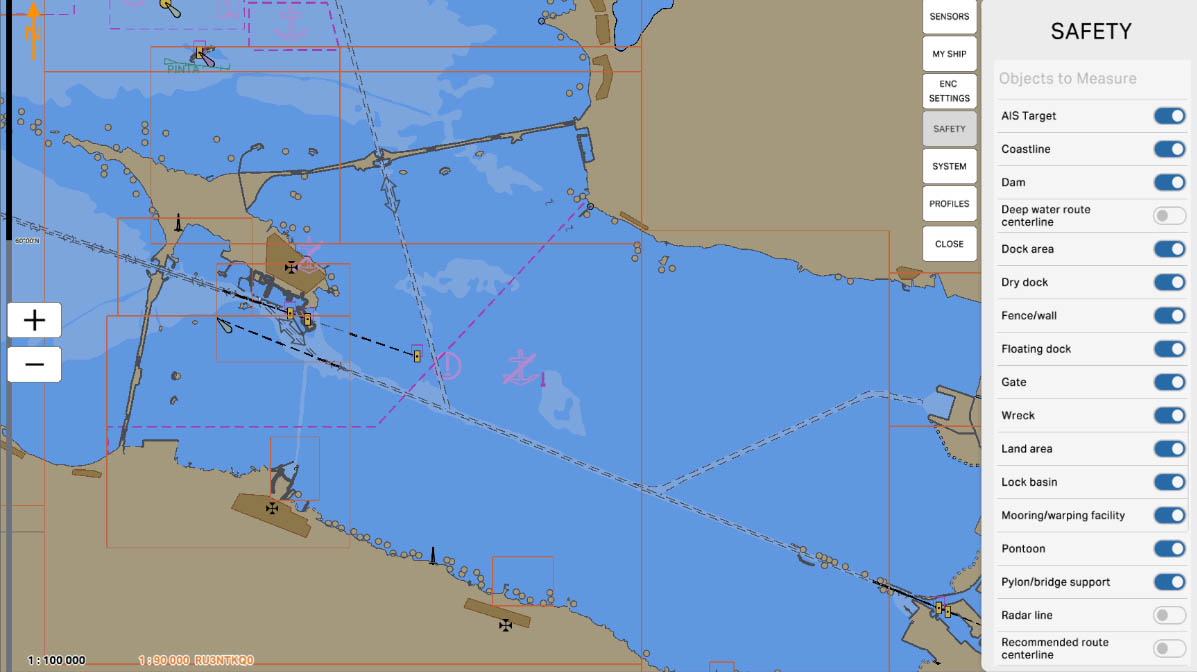
'Objects to Measure' is a section where users can select and include active objects in distance measurements on the nautical chart. These objects may include other vessels, buoys, coastal landmarks, or any other elements that can be highlighted or identified as active.
SAFETY SETTINGS

55
57
'Coastline' - this option allows the user to include data about the coastline in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. Taking the coastline into account is an important aspect of navigation when planning routes and measuring distances from the vessel to the shore.
Objects to Measure
58
'Dam' - the option provides the ability to include data about dams in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. This can be useful for navigation in areas with dams, as mariners need to take these objects into account when planning routes and measuring distances.
Objects to Measure
59
'Deep Water Route Centerline' - this option allows including data about the centerline of a deep-water route in distance measurements or other operations on the electronic chart. Deep-water routes are specially marked routes designed for vessels with a significant draft to ensure safe navigation through deep waters. Enabling this option can be useful when navigating in areas with deep-water routes.
Objects to Measure
60
'Dock Area' - this option allows including data about dock areas in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. In navigation, it is important to take into account distances from the vessel to areas with docks, such as ports or docks, and enabling this option can assist mariners in route planning and ensuring safety in dock areas.
Objects to Measure
61
'Dry Dock' - this option allows including data about dry docks in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. Dry docks are specialized structures used to lift vessels out of the water for repair or maintenance purposes. Enabling this option can be useful for navigation in areas with dry docks, helping to take these objects into account when planning routes and measuring distances.
Objects to Measure
62
'Fence/Wall' - this option allows including data about fences or walls in distance measurements or other operations on the maritime chart. In navigation, it is important to consider distances from the vessel to obstacles such as fences or walls, and enabling this option can assist mariners in route planning and ensuring safety in areas with such objects.
Objects to Measure
63
'Floating Dock' - this option allows including data about floating docks in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. Floating docks are structures capable of rising and sinking in the water, designed to lift vessels from the water for repair or maintenance work. Enabling this option can be useful for navigation in areas with floating docks, helping to consider these objects when planning routes and measuring distances.
Objects to Measure
64
'Gate' - this option allows including data about gates in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. In navigation, it is important to consider distances from the vessel to gates, and enabling this option can assist navigators in planning routes and ensuring safety in areas with gates. This may relate to gates in straits, channels, or other critical maritime passages.
Objects to Measure
65
'Wreck' - this option allows including data about wrecks or sunken objects in distance measurements or other operations on the maritime chart. Wrecks can pose a danger to navigation, and taking their location into account is crucial for maritime safety. Enabling this option can help navigators avoid potential hazardous areas and take precautionary measures when planning routes.
Objects to Measure
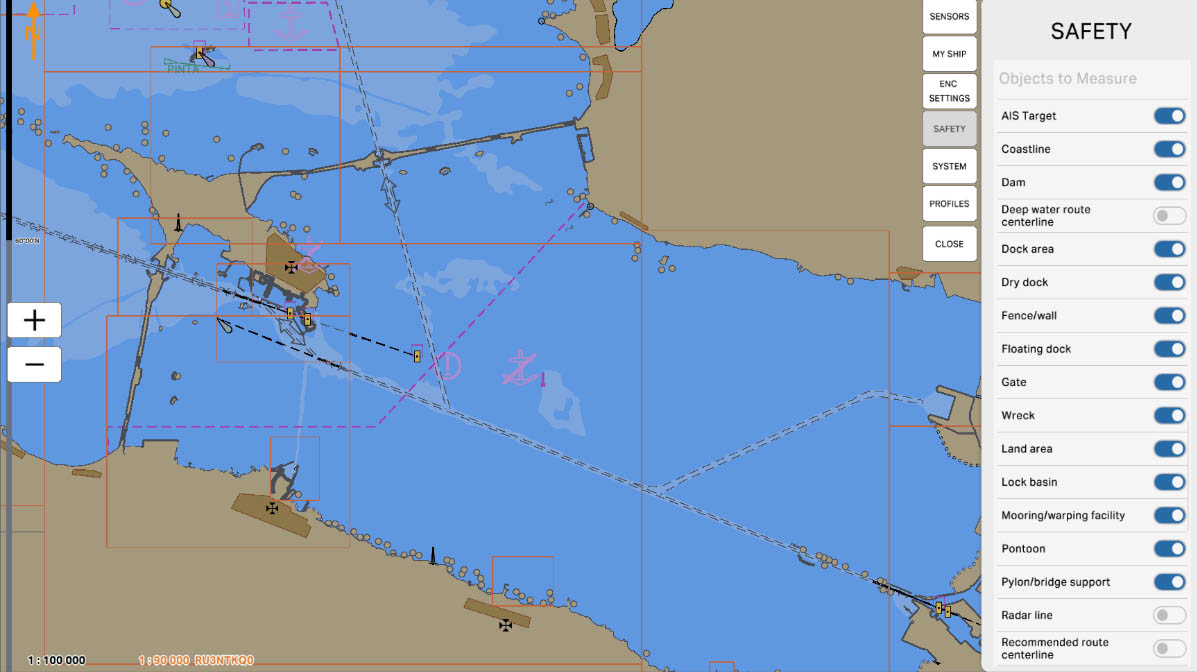
66
'Land Area' - This option allows including data about land in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. Accounting for the location of land is crucial for navigation, as it enables mariners to better understand the surrounding environment and plan routes accurately, taking into consideration coastal areas and landscape features.
Objects to Measure
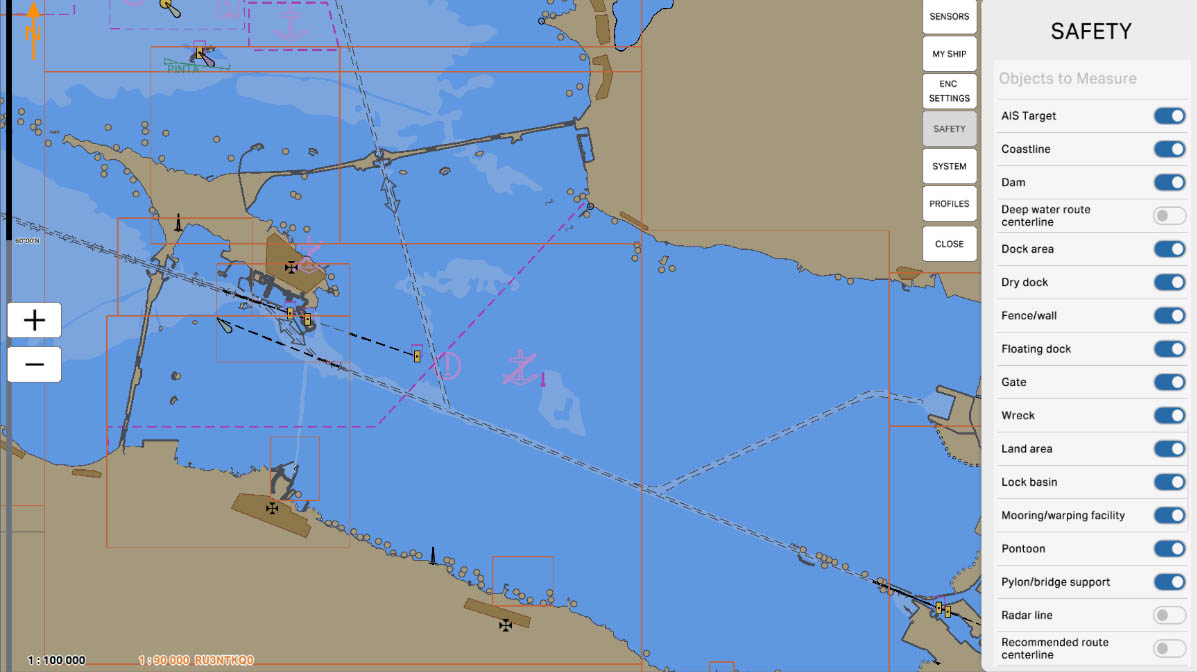
67
'Lock Basin' - this option allows including data about locks (hydraulic gates) in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. Locks are used in navigation systems to raise or lower the water level, facilitating the passage of vessels through different levels within water systems, such as canals or rivers. Enabling this option helps mariners take locks into account when planning routes and ensures safety in navigation areas using hydraulic gates.
Objects to Measure
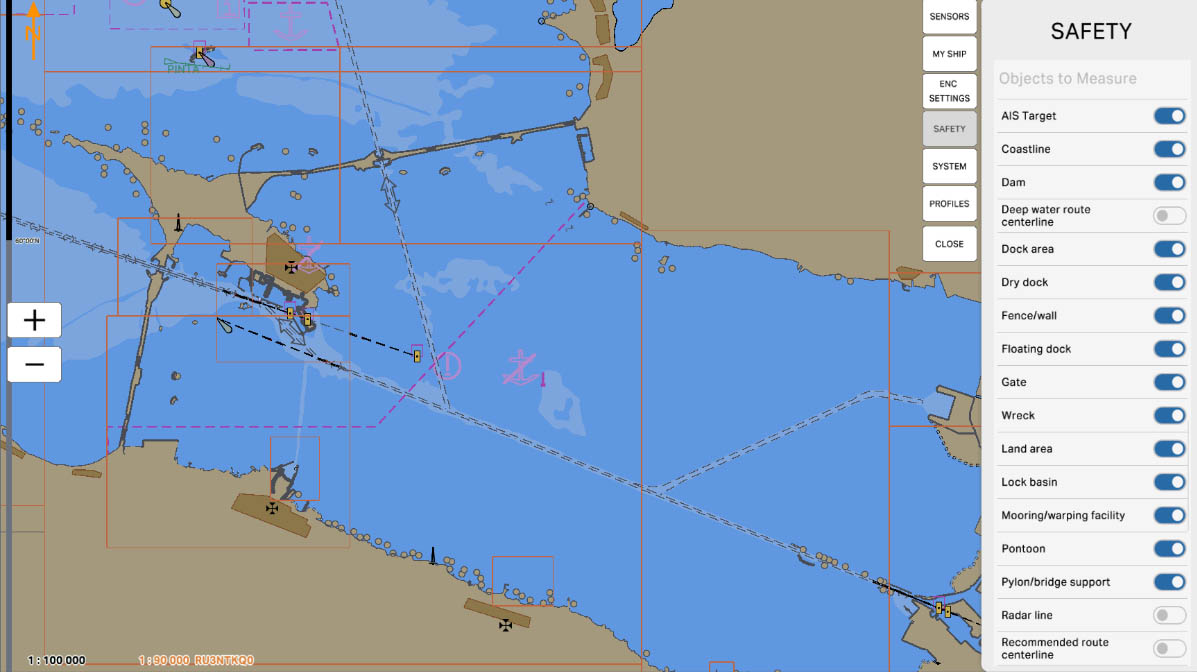
68
'Mooring/Warping Facility' - this option allows including data about mooring and warping facilities in distance measurements or other operations on the maritime chart. These objects encompass structures and equipment designed to secure or move vessels in ports, docks, or other mooring locations. Enabling this option helps navigators take into account the location of mooring and warping facilities when planning routes and ensuring safety in ports and other waterways.
Objects to Measure
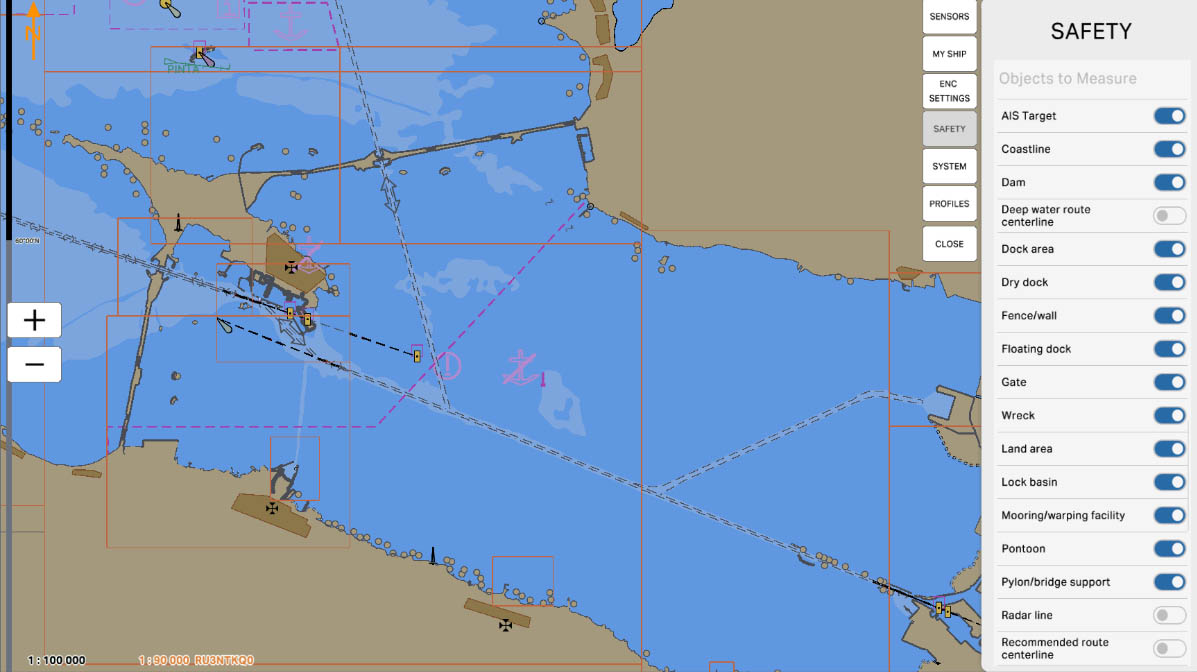
69
'Pontoon' - this option allows including data about pontoons in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. A pontoon is a floating platform or structure often used for mooring vessels or other maritime operations. Enabling this option can be useful for mariners navigating areas where pontoons are present, such as ports or coastal zones.
Objects to Measure
70
'Pylon/Bridge Support' - this option allows including data about bridge supports in distance measurements or other operations on the maritime chart. Bridge supports, also known as pylons, are structures that support bridges. Enabling this option can be useful for navigators when navigating in areas with bridges, allowing them to take these structures into account when planning routes and measuring distances.
Objects to Measure
71
'Radar Line' - this option allows including data about radar lines in distance measurements or other operations on the maritime chart. Radar lines represent areas where radar equipment is operating, and their consideration is crucial for navigation to avoid collisions and ensure the safety of vessels. Enabling this option helps mariners take radar parameters into account when planning routes and performing other operations on the maritime chart.
Objects to Measure
72
'Recommended Route Centerline' is an option that allows including data about the centerline of a recommended route in distance measurements or other operations on the electronic chart display and information system (ECDIS) map. Recommended routes provide optimal pathways for vessels, ensuring safe and efficient navigation through specific waterways. Enabling this option can be useful for navigators when sailing along recommended routes and ensuring compliance with them.
Objects to Measure

73
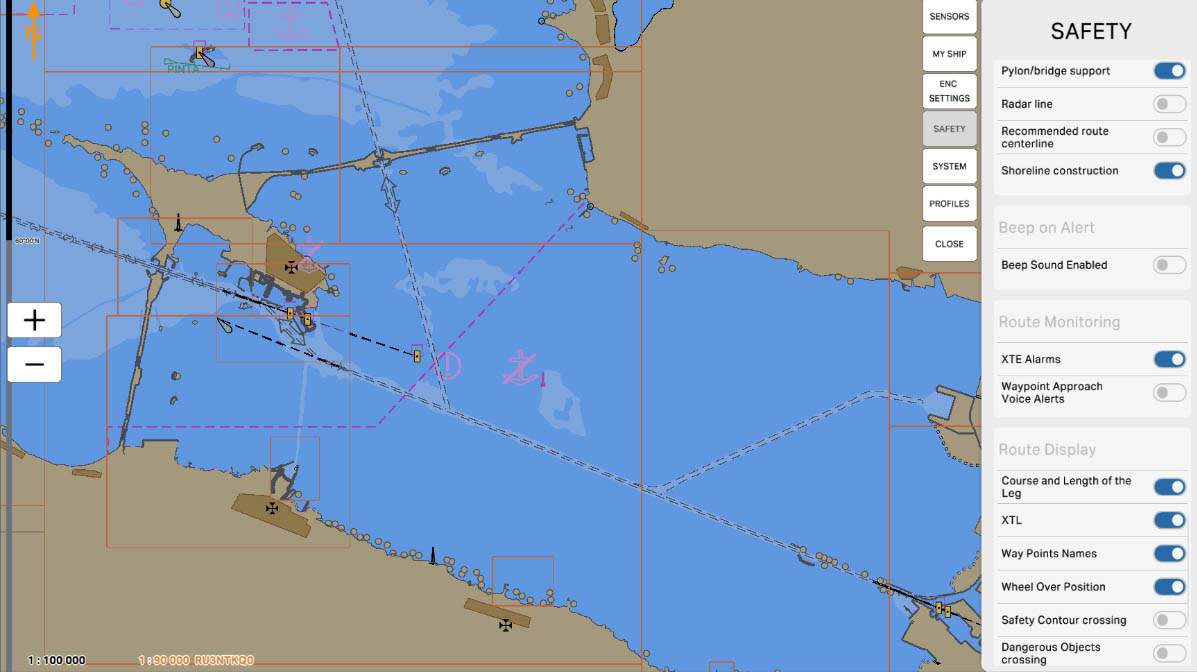
'Shoreline Construction' - this option allows including data about constructions along the shore in distance measurements or other operations on the nautical chart. It may encompass various structures such as piers, docks, cargo handling stations, and other facilities related to the shoreline. Enabling this option helps navigators take into account shoreline constructions when planning routes and measuring distances, ensuring the safety of navigation near the coast.
Objects to Measure
75
'Beep Sound Enabled' is an option to enable or disable sound signals for warnings and alarms. When this option is enabled, the system will play sound signals in the event of warnings or alarms, alerting mariners to potential dangers or situations that require attention. If the option is disabled, sound signals will not be played, and warnings will be visible only visually on the screen.
Beep on Alert
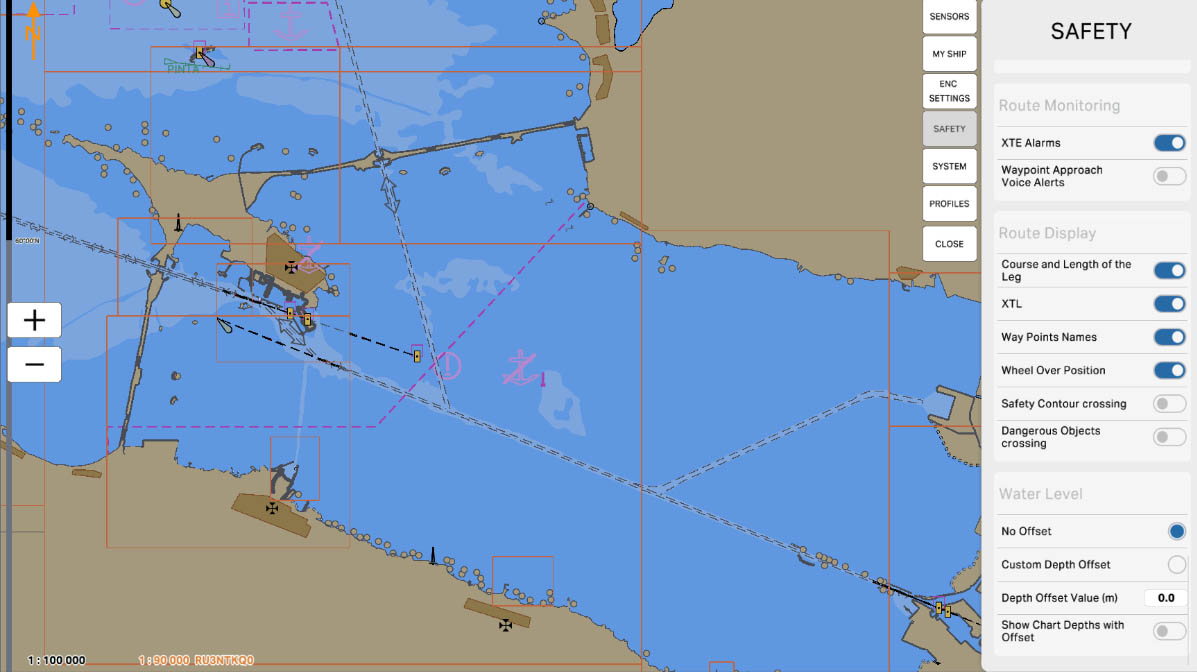
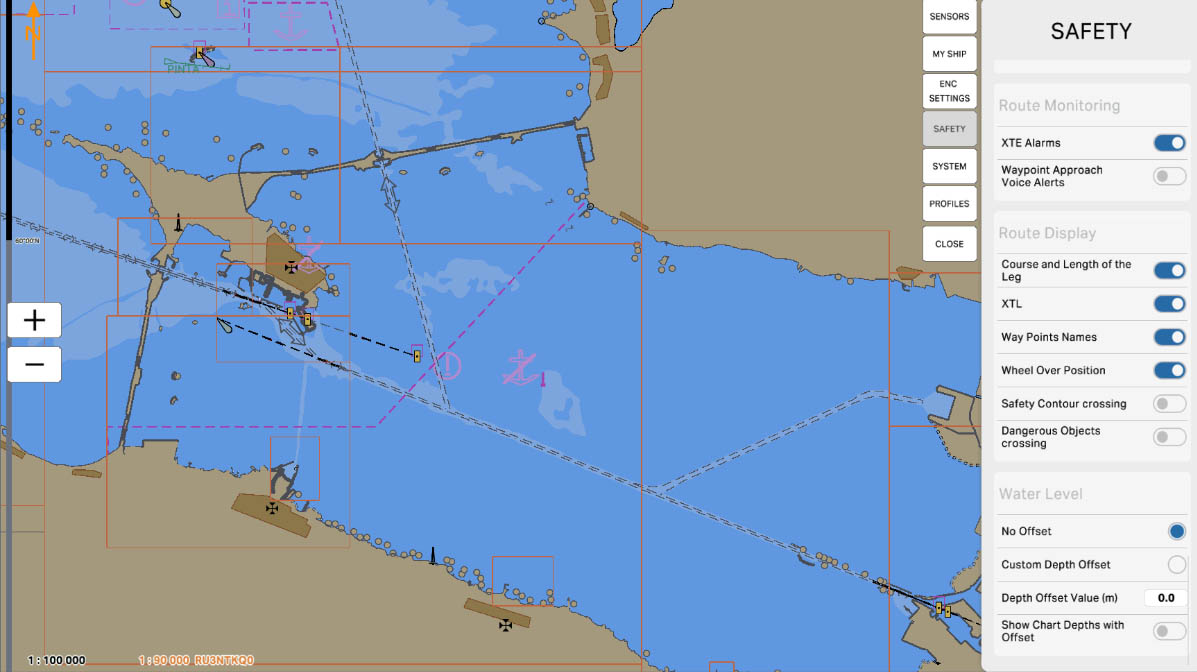
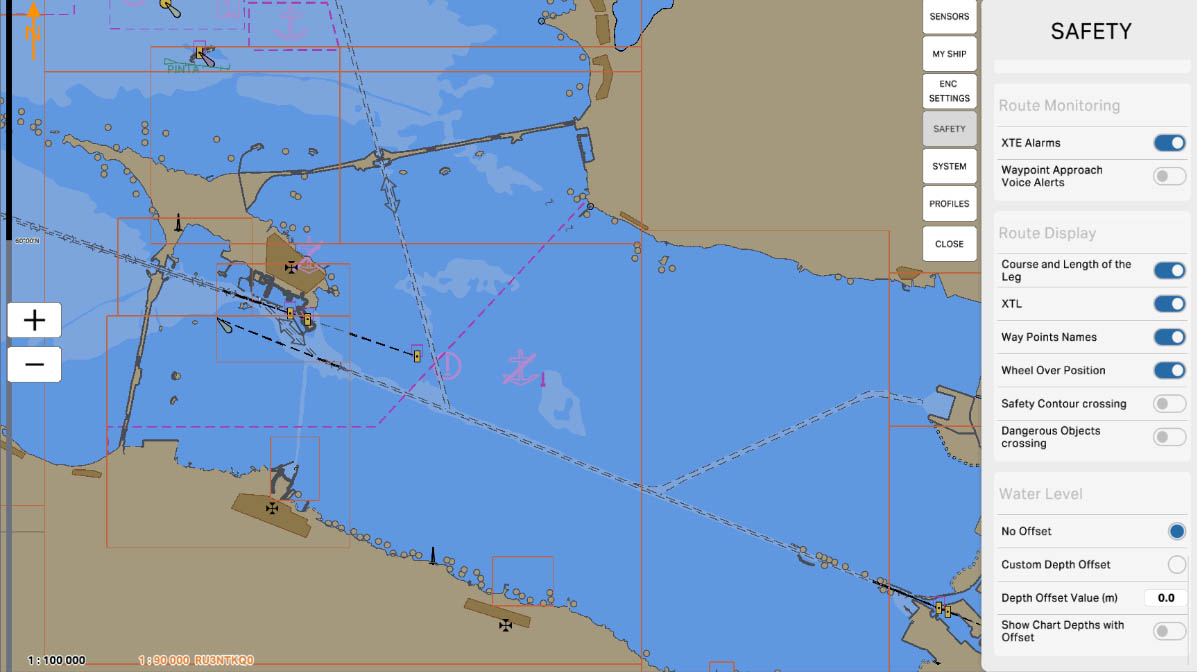
'Route Monitoring' refers to the route monitoring feature on the Electronic Chart Display and Information System (ECDIS). The options in this section allow the system to track and warn of any potential hazards or deviations from the specified route of the vessel.
SAFETY SETTINGS

76
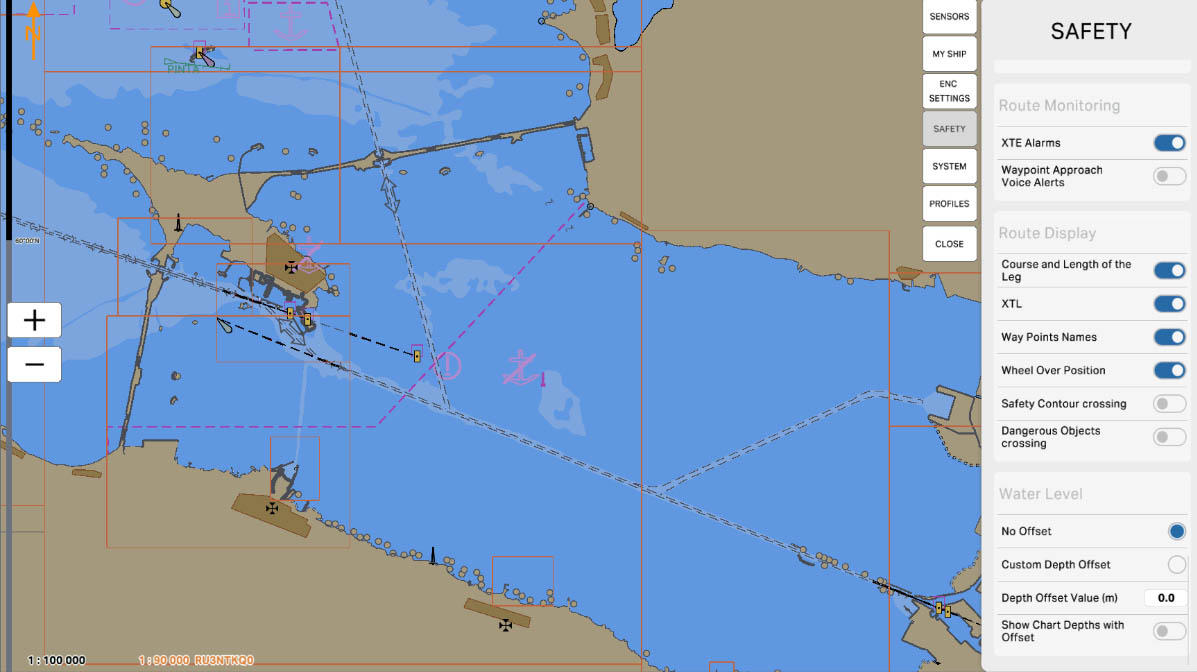
77
'XTE Alarms' is an alert option on the Electronic Chart Display and Information System (ECDIS) and is associated with the 'Cross-Track Error' (XTE) monitoring function. XTE represents the distance between the vessel and the planned route, measured in the plane perpendicular to the route.
Enabling the 'XTE Alarms' option allows activating alerts related to the vessel deviating from the planned route. These alerts may include sound signals, visual indicators to warn the navigator of potential deviations, ensuring navigation safety.
Enabling the 'XTE Alarms' option allows activating alerts related to the vessel deviating from the planned route. These alerts may include sound signals, visual indicators to warn the navigator of potential deviations, ensuring navigation safety.
Route Monitoring
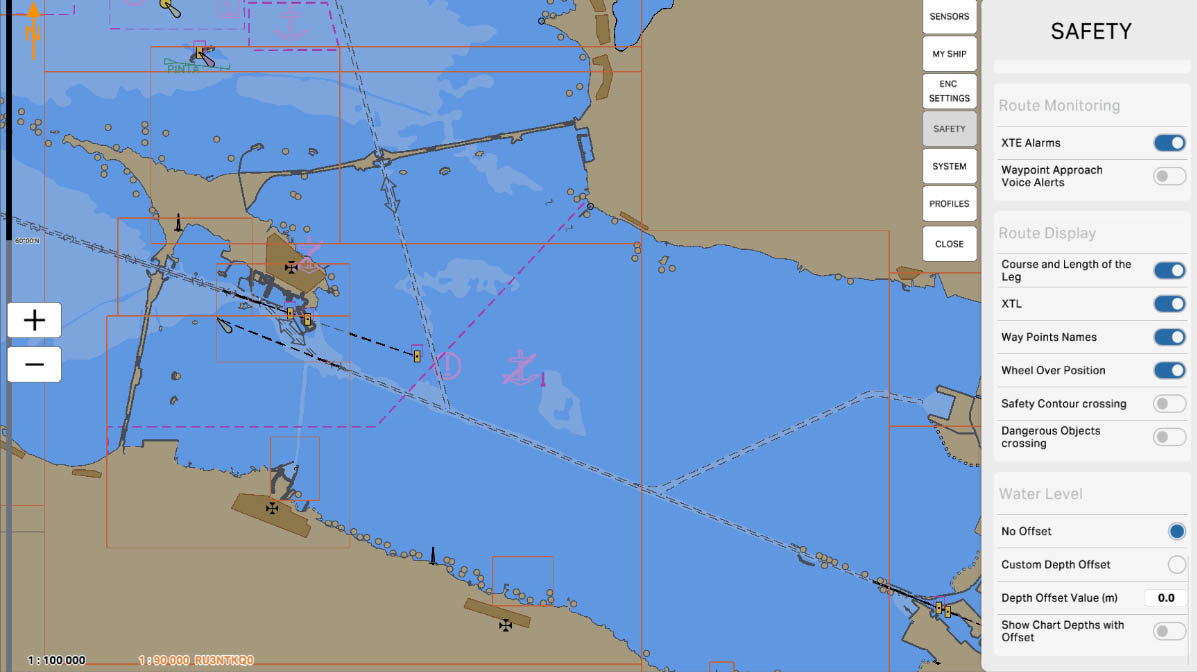
78
'Waypoint Approach Voice Alerts' - when this option is enabled, the system can provide voice alerts when approaching a waypoint on the route. These voice signals serve to notify the navigator that the vessel is approaching the next waypoint, aiding them in efficiently following the planned route.
Route Monitoring
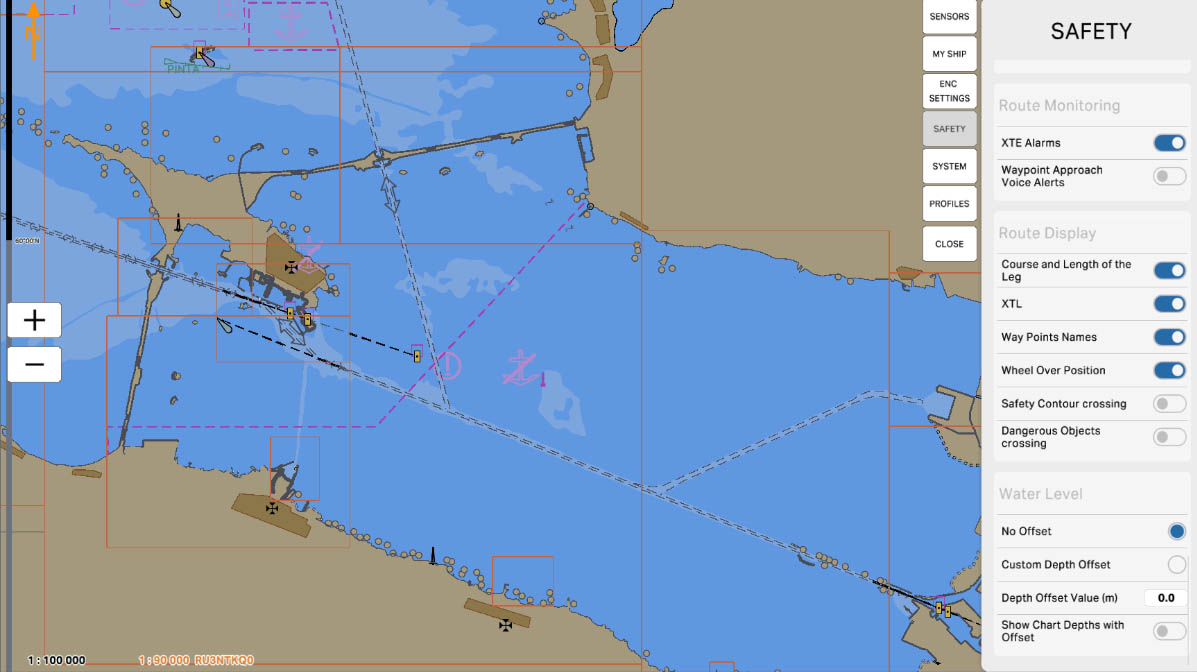
79
'Route Display' - This section provides options and parameters related to the display of the vessel's route on the electronic chart. In this section, the user can configure the visualization of the route to ensure a more convenient perception of route information on the screen.
SAFETY SETTINGS

80
'Show Course and Length of the Leg' is an option that allows displaying on the chart information about
the course and length of each leg of the route. This feature provides a visual representation of the vessel's
heading and the distance remaining to the next waypoint or the final destination of the route.
the course and length of each leg of the route. This feature provides a visual representation of the vessel's
heading and the distance remaining to the next waypoint or the final destination of the route.
SAFETY SETTINGS

81
'Show XTL' is an option that displays information about the 'Cross-Track Limit' (XTL). XTL is the distance on both sides of the intended route within which a vessel is considered to be on track. Enabling the 'Show XTL' option allows for the visual tracking of the boundaries within which the vessel may deviate from the intended route. This is useful for the navigator to assess how much the vessel is deviating from the planned route and whether it remains within the acceptable deviation limits (XTL)
SAFETY SETTINGS

82
'Show Waypoints Names' is an option that enables the display of names (or labels) of waypoints on the electronic chart. When this option is activated, the names of waypoints will be visible on the screen, providing the navigator with additional information about each specific point of the route. This can be useful for ease of orientation and understanding the sequence of waypoints.
SAFETY SETTINGS

83
'Show Wheel Over Position' is an option that allows displaying information about the ship's position relative to the steering device. When this option is enabled, the map will show the ship's position in
relation to its steering device, providing the navigator with valuable information for maneuvering and controlling the vessel. This feature offers a visual representation of how the ship is oriented concerning
the set course.
relation to its steering device, providing the navigator with valuable information for maneuvering and controlling the vessel. This feature offers a visual representation of how the ship is oriented concerning
the set course.
SAFETY SETTINGS
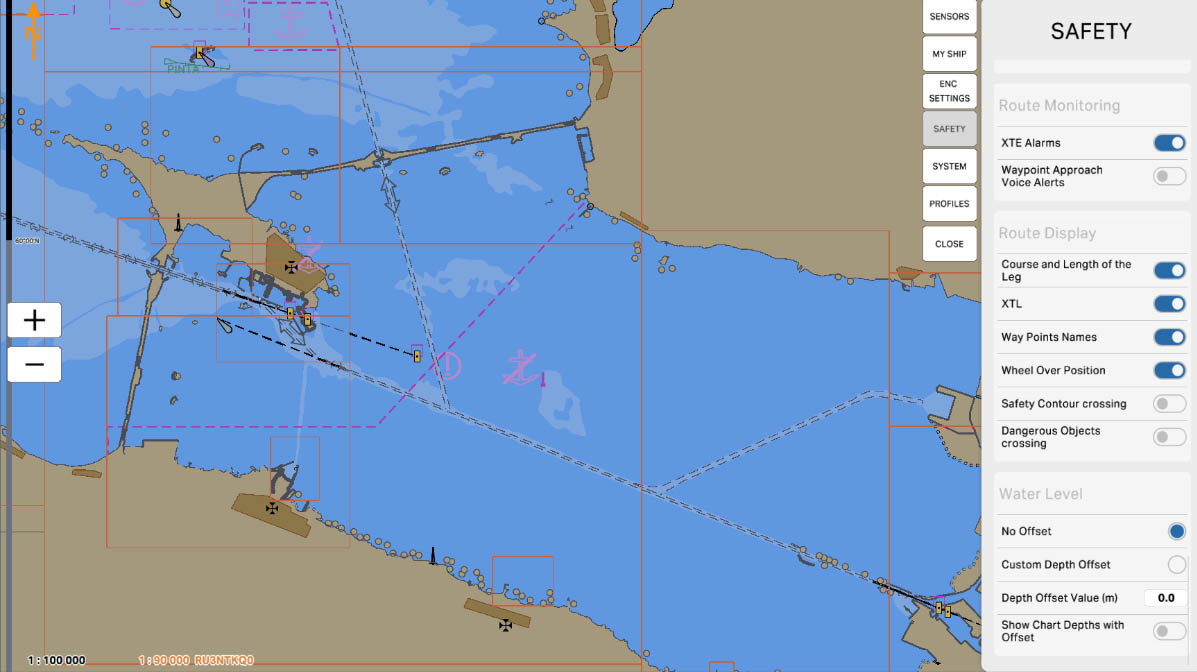
84
The "Safety Contour Crossing" parameter is used to configure the route monitoring system to track the vessel's approach to the safety contour. When enabled, if the vessel approaches the safety contour within the user-defined distance or time, the system will emit an audible alarm. This alert warns the crew of the potential risk of grounding or collision with underwater obstacles, allowing them to take timely action to ensure safe navigation.
Route Monitoring
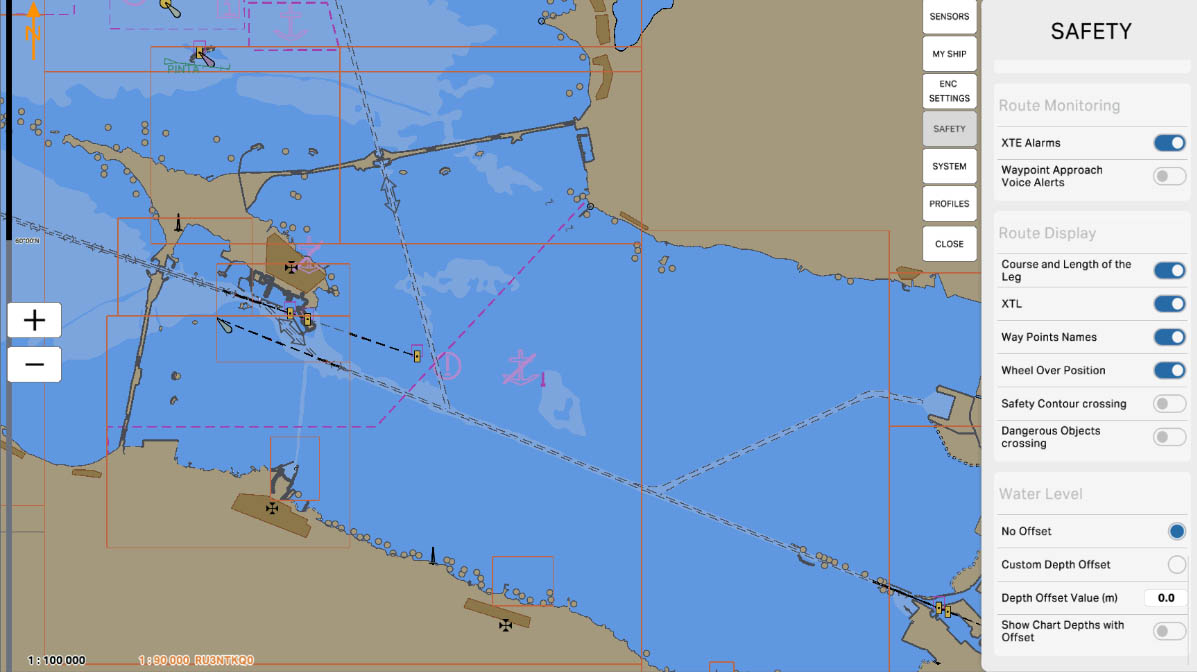
85
The "Dangerous Objects Crossing" parameter is used to configure the route monitoring system to track the vessel's approach to dangerous objects such as reefs, shoals, or other underwater hazards. When enabled, if the vessel approaches the crossing of a specified dangerous object within the user-defined distance or time, the system will emit an audible alarm. This alert allows the crew to promptly respond to potential threats and take action to prevent collisions or other incidents.
Route Monitoring
86
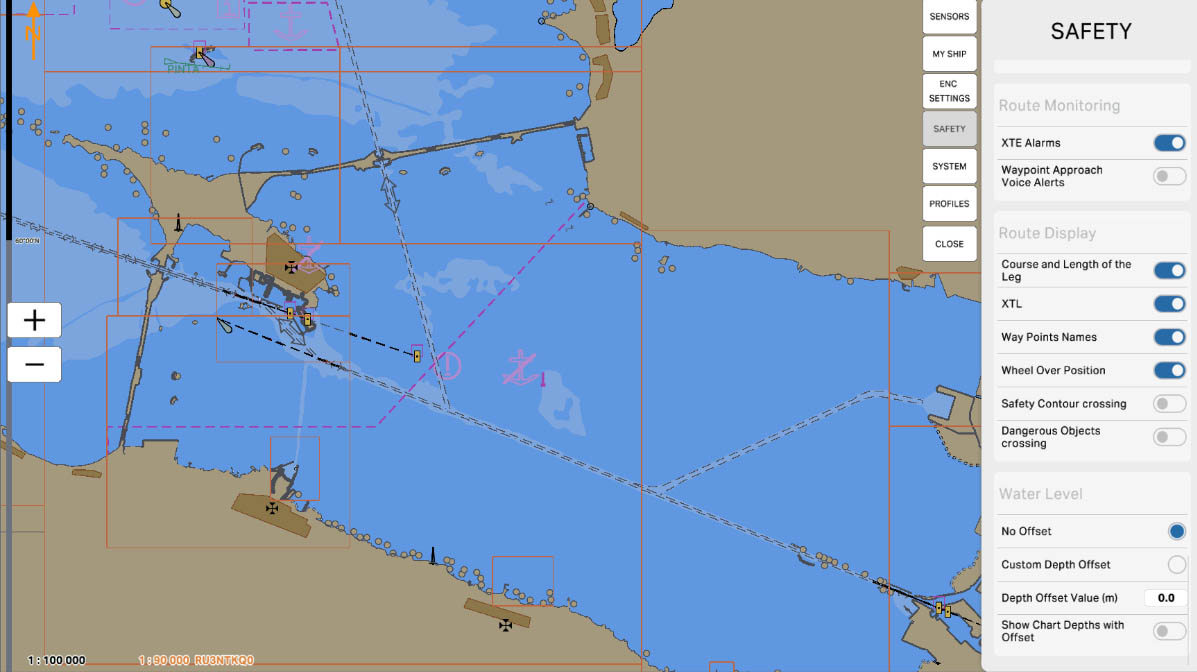
'Water Level' in the safety settings section is related to monitoring and managing water levels. This section includes options and parameters associated with changes in water levels in specific maritime areas.
The 'Water Level' settings can be crucial for mariners, especially when approaching coastal areas where changes in water levels can be caused by tides, storms, or other factors. These settings can alert mariners to potential dangers related to changes in water levels, contributing to navigation safety.
The 'Water Level' settings can be crucial for mariners, especially when approaching coastal areas where changes in water levels can be caused by tides, storms, or other factors. These settings can alert mariners to potential dangers related to changes in water levels, contributing to navigation safety.
SAFETY SETTINGS
87
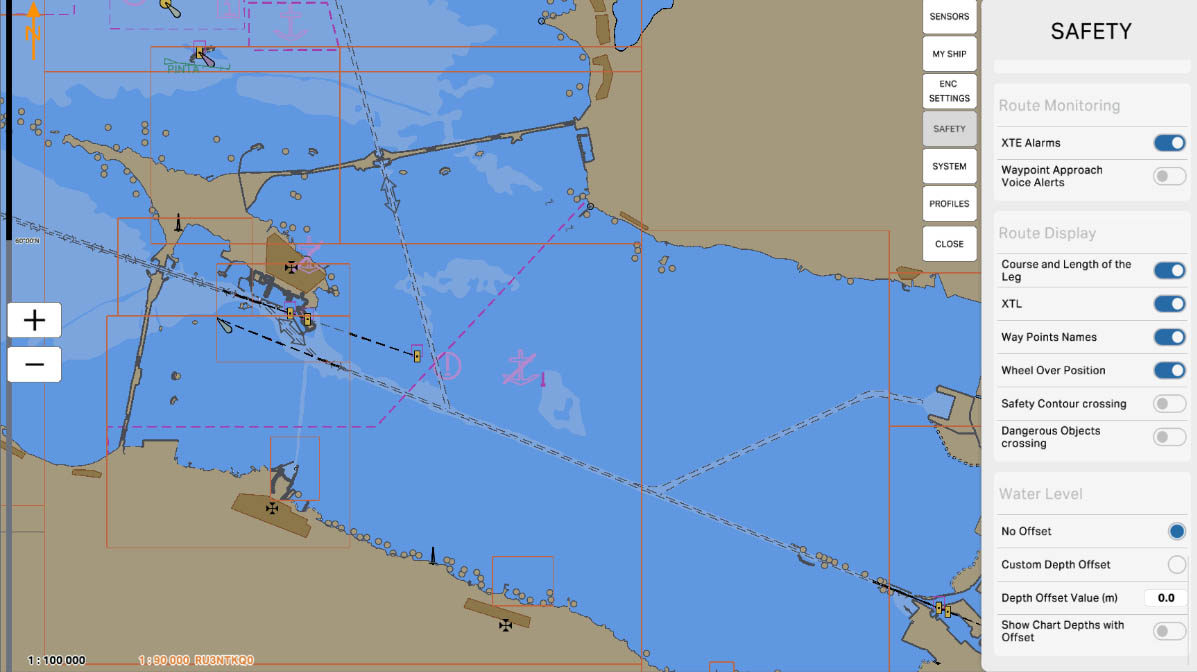
The 'No Offset' option indicates the absence of any offset or correction in water level measurements. When the 'No Offset' option is selected, the system does not apply any additional corrections to the measured water level data, and the displayed values remain unchanged. This can be important for accurately tracking the water level in a marine region without any corrections or compensations.
Water Level
88
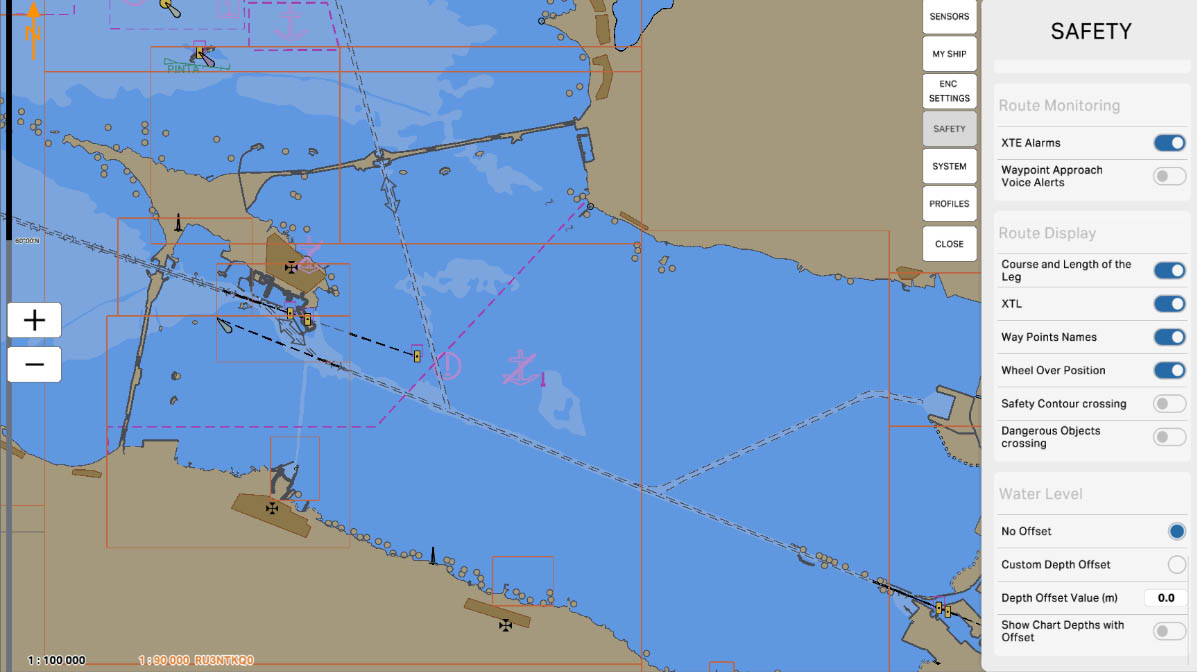
'Custom Depth Offset' is an option that allows the user to enter a custom, individual depth offset value. This offset can be applied to the measured water level values to correct the data. For example, if the vessel is equipped with additional measurement instruments, the user can manually input an offset to account for the specific characteristics of the system.
This setting enables refining the water level data according to the specific features of the vessel or the area, providing a more accurate display of information on the nautical chart.
This setting enables refining the water level data according to the specific features of the vessel or the area, providing a more accurate display of information on the nautical chart.
Water Level

89
'Depth Offset Value (m)' is a parameter that allows entering a numerical value for depth offset in meters. This parameter is used to correct measured water level data, enabling the user to refine the values considering the vessel's characteristics or specific geographical features.
By entering a specific numerical value into this parameter, the user determines how much to adjust the measured water level data. This can be useful, for example, when using additional depth measurement instruments.
By entering a specific numerical value into this parameter, the user determines how much to adjust the measured water level data. This can be useful, for example, when using additional depth measurement instruments.
Water Level
90
'Show Chart Depths with Offset' — when this option is enabled, the depths displayed on the nautical chart will be adjusted considering the set water level offset.
This is important for mariners as they can see depths adjusted for changes in the water level. It is especially useful in coastal areas where tides or other factors may affect the water level and depths. By enabling this option, mariners gain a more accurate representation of the actual water depth during navigation.
This is important for mariners as they can see depths adjusted for changes in the water level. It is especially useful in coastal areas where tides or other factors may affect the water level and depths. By enabling this option, mariners gain a more accurate representation of the actual water depth during navigation.
Water Level
The "5.4. Safety Settings" section has been completed.
Success!